The album version of this song was released by Fleetwood Mac on Mirage in 1982, and my dad had it on a tape in his car for most of the ’80s.
But this, this is something else.
The album version of this song was released by Fleetwood Mac on Mirage in 1982, and my dad had it on a tape in his car for most of the ’80s.
But this, this is something else.
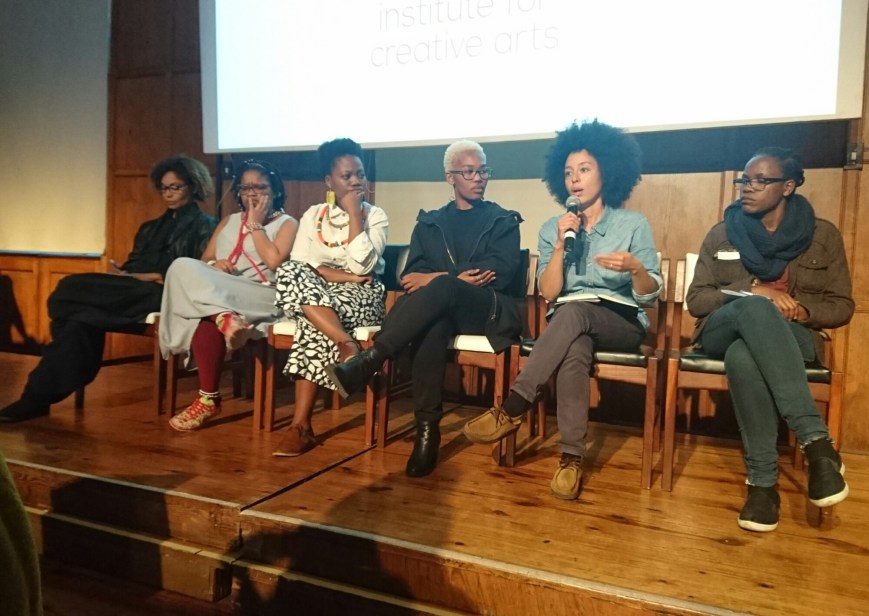

L-R: jackï job, Dee Moholo, Koleka Putuma, Khanyi Mbongwa (Vasiki), Ilze Wolff, Lois Anguria
The most decolonised academic space I have yet had the joy of experiencing. The conference continues today. If you’re in Cape Town, come. It’s free!
HERE is the programme. 🌸
From John Peel’s ‘Night Ride’ session, recorded 5 August 1969 and broadcast the day after.
Will I ever find my real voice?
THIS. This is so on point.
1995. Footage of Catherine Deneuve from Repulsion (1965).
“The laws of macro- and microcosm are alike. Travel in the interior is as a voyage in outer space: we must in each case burst past the circumference of our surface – our here-space and now-time – and, cut loose from the anchorage of an absolute, fixed center, enter worlds where the relationship of parts is the sole gravity. When the sun sets, the stars become apparent; when our eyes close out the light to sleep, there rises in the night-eye the constellation by which sleep-walkers plot their incalculable accuracies. By day we move according to desire and decision; by night Noctambulo advances without moving, led by the twins Gemini (as the eyes are twins or as the I of night is twin to that of day). It is by the dark geometry of such celestial navigation that the day‘s erratic negotiations are corrected and reconciled into the total orbits of our lives.
The film is in the negative. The blackness of night erases all horizon and, released from the leveling pressure of this plane, the movements both of the dancers and of the camera become as four-dimensional and directional as those of birds in air or fish in water.”
– Maya Deren: Chamber Films, program notes for a presentation, 1960
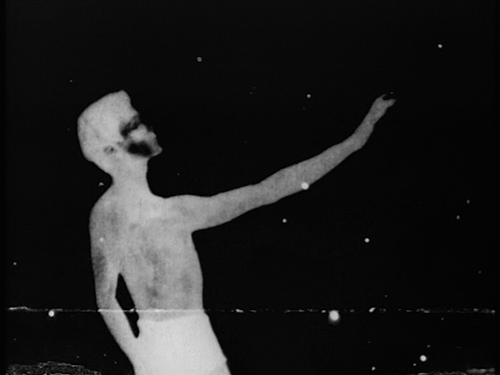
#Title: The Very Eye of Night
#Director: Maya Deren
#Year of Production: 1958
#Duration: 00:15:00
#Choregraphy: Antony Tudor, Metropolitan Opera Ballet School
#Dancers / Actors: Philp Salem, Rosemary Williams, Richard Englund, Richard Sandifer, Don Freisinger, Patricia Ferrier, Barbara Levin, Bud Bready, Genaro Gomez
#Camera: Maya Deren
#Editing: Maya Deren
#Foley Assistance: Harrison Starr
#Sound: Louis and Bebe Barron
#Music: Teiji Ito
Hélène Cixous’ essay “Castration or Decapitation?” discusses the binary construction of sexuality and society, and how the feminine is defined by the negative: a woman is not a man because she lacks a penis. This “lack” keeps the female subject to definition by the male, as it is seen that because she is the “negative” pole to the man’s “positive”, the woman is concomitantly un-informed, and that therefore it is the position of the man to inform the woman. This imposed silence is what decapitates the feminine metaphorically, precluding her from speaking anything of meaning.
The following is an excerpt from this brilliant essay, translated by Annette Kuhn and published in Signs, Vol. 7, No. 1 (Autumn, 1981), pp. 41-55 (University of Chicago Press) – read the full essay HERE.
* * * * *
… It’s hard to imagine a more perfect example of a particular relationship between two economies: a masculine economy and a feminine economy, in which the masculine is governed by a rule that keeps time with two beats, three beats, four beats, with pipe and drum, exactly as it should be. An order that works by inculcation, by education. It’s always a question of education: an education that consists of trying to make a soldier of the feminine by force, the force history keeps reserved for woman, the “capital” force that is effectively decapitation. Women have no choice other than to be decapitated. The moral is that if they don’t actually lose their heads by the sword, they only keep them on condition that they lose them – lose them, that is, to complete silence, turned into automatons.
It’s a question of submitting feminine disorder, its laughter, its inability to take the drumbeats seriously, to the threat of decapitation. If man operates under the threat of castration, if masculinity is culturally ordered by the castration complex, it might be said that the backlash, the return, on women of this castration anxiety is its displacement as decapitation, execution, of woman, as loss of her head.
We are led to pose the woman question to history in quite elementary forms like, “Where is she? Is there any such thing as woman?” At worst, many women wonder whether they even exist. They feel they don’t exist and wonder if there has ever been a place for them. I am speaking of woman’s place,from woman’s place, if she takes (a) place.
In La Jeune Née I made use of a story that seemed to me particularly expressive of woman’s place: the story of Sleeping Beauty. Woman, if you look for her, has a strong chance of always being found in one position: in bed. In bed and asleep-“laid (out).” She is always to be found on or in a bed: Sleeping Beauty is lifted from her bed by a man because, as we all know, women don’t wake up by themselves: man has to intervene, you understand. She is lifted up by the man who will lay her in her next bed so that she may be confined to bed ever after, just as the fairy tales say.
And so her trajectory is from bed to bed: one bed to another, where she can dream all the more. There are some extraordinary analyses by Kierkegaard on women’s “existence”- or that part of it set aside for her by culture-in which he says he sees her as sleeper. She sleeps, he says, and first love dreams her and then she dreams of love. From dream to dream, and always in second position. In some stories, though, she can be found standing up, but not for long.
Take Little Red Riding Hood as an example: it will not, I imagine, be lost on you that the “red riding hood” in question is a little clitoris. Little Red Riding Hood basically gets up to some mischief: she’s the little female sex that tries to play a bit and sets out with her little pot of butter and her little jar of honey. What is interesting is that it’s her mother who gives them to her and sends her on an excursion that’s tempting precisely because it’s forbidden: Little Red Riding Hood leaves one house, mommy’s house, not to go out into the big wide world but to go from one house to another by the shortest route possible: to make haste, in other words, from the mother to the other.
The other in this case is grandmother, whom we might imagine as taking the place of the “Great Mother,” because there are great men but no great women: there are Grand-Mothers instead. And grandmothers are always wicked: she is the bad mother who always shuts the daughter in whenever the daughter might by chance want to live or take pleasure. So she’ll always be carrying her little pot of butter and her little jar of honey to grandmother, who is there as jealousy … the jealousy of the woman who can’t let her daughter go.
But in spite of all this Little Red Riding Hood makes her little detour, does what women should never do, travels through her own forest. She allows herself the forbidden … and pays dearly for it: she goes back to bed, in grandmother’s stomach. The Wolf is grandmother, and all women recognize the Big Bad Wolf! We know that always lying in wait for us somewhere in some big bed is a Big Bad Wolf.
The Big Bad Wolf represents, with his big teeth, his big eyes, and his grandmother’s looks, that great Superego that threatens all the little female red riding hoods who try to go out and explore their forest without the psychoanalyst’s permission. So, between two houses, between two beds, she is laid, ever caught in her chain of metaphors, metaphors that organize culture . . . ever her moon to the masculine sun, nature to culture, concavity to masculine convexity, matter to form, immobility/inertia to the march of progress, terrain trod by the masculine footstep, vessel… While man is obviously the active, the upright, the productive… and besides, that’s how it happens in History.
This opposition to woman cuts endlessly across all the oppositions that order culture. It’s the classic opposition, dualist and hierarchical. Man/Woman automatically means great/small, superior/inferior… means high or low, means Nature/History, means transformation/inertia. In fact, every theory of culture, every theory of society, the whole conglomeration of symbolic systems-everything, that is, that’s spoken, everything that’s organized as discourse, art, religion, the family, language, everything that seizes us, everything that acts on us – it is all ordered around hierarchical oppositions that come back to the man/ woman opposition, an opposition that can only be sustained by means of a difference posed by cultural discourse as “natural,” the difference between activity and passivity. It always works this way, and the opposition is founded in the couple [binary]. A couple posed in opposition, in tension, in conflict… a couple engaged in a kind of war in which death is always at work – and I keep emphasizing the importance of the opposition as couple, because all this isn’t just about one word; rather everything turns on the Word: everything is the Word and only the Word. To be aware of the couple, that it’s the couple that makes it all work, is also to point to the fact that it’s on the couple that we have to work if we are to deconstruct and transform culture. The couple as terrain, as space of cultural struggle, but also as terrain, as space demanding, insisting on, a complete transformation in the relation of one to the other. And so work still has to be done on the couple … on the question, for example, of what a completely different couple relationship would be like, what a love that was more than merely a cover for, a veil of, war would be like.
I said it turns on the Word: we must take culture at its word, as it takes us into its Word, into its tongue. You’ll understand why I think that no political reflection can dispense with reflection on language, with work on language. For as soon as we exist, we are born into language and language speaks (to) us, dictates its law, a law of death: it lays down its familial model, lays down its conjugal model, and even at the moment of uttering a sentence, admitting a notion of “being,” a question of being, an ontology, we are already seized by a certain kind of masculine desire, the desire that mobilizes philosophical discourse. As soon as the question “What is it?” is posed, from the moment a question is put, as soon as a reply is sought, we are already caught up in masculine interrogation. I say “masculine interrogation”: as we say so-and-so was interrogated by the police. And this interrogation precisely involves the work of signification: “What is it? Where is it?” A work of meaning, “This means that,” the predicative distribution that always at the same time orders the constitution of meaning. And while meaning is being constituted, it only gets constituted in a movement in which one of the terms of the couple is destroyed in favor of the other.
“Look for the lady,” as they say in the stories… “Cherchez la femme”– we always know that means: you’ll find her in bed. Another question that’s posed in History, rather a strange question, a typical male question, is: “What do women want?” The Freudian question, of course. In his work on desire, Freud asks somewhere, or rather doesn’t ask, leaves hanging in the air, the question “What do women want?” Let’s talk a bit about this desire and about why/how the question “What do women want?” gets put, how it’s both posed and left hanging in the air by philosophical discourse, by analytic discourse (analytic discourse being only one province of philosophical discourse), and how it is posed, let us say, by the Big Bad Wolf and the Grand-Mother.
“What does she want?” Little Red Riding Hood knew quite well what she wanted, but Freud’s question is not what it seems: it’s a rhetorical question. To pose the question “What do women want?” is to pose it already as answer, as from a man who isn’t expecting any answer, because the answer is “She wants nothing.” … “What does she want? … Nothing!” Nothing because she is passive. The only thing man can do is offer the question “What could she want, she who wants nothing?” Or in other words: “Without me, what could she want?”
Old Lacan takes up the slogan “What does she want?” when he says, “A woman cannot speak of her pleasure.” Most interesting! It’s all there, a woman cannot, is unable, hasn’t the power. Not to mention “speaking”: it’s exactly this that she’s forever deprived of. Unable to speak of pleasure = no pleasure, no desire: power, desire, speaking, pleasure, none of these is for woman. And as a quick reminder of how this works in theoretical discourse, one question: you are aware, of course, that for Freud/Lacan, woman is said to be “outside the Symbolic”: outside the Symbolic, that is outside language, the place of the Law, excluded from any possible relationship with culture and the cultural order. And she is outside the Symbolic because she lacks any relation to the phallus, because she does not enjoy what orders masculinity – the castration complex.
Woman does not have the advantage of the castration complex – it’s reserved solely for the little boy. The phallus, in Lacanian parlance also called the “transcendental signifier,” transcendental precisely as primary organizer of the structure of subjectivity, is what, for psychoanalysis, inscribes its effects, its effects of castration and resistance to castration and hence the very organization of language, as unconscious relations, and so it is the phallus that is said to constitute the a priori condition of all symbolic functioning. This has important implications as far as the body is concerned: the body is not sexed, does not recognize itself as, say, female or male without having gone through the castration complex.
What psychoanalysis points to as defining woman is that she lacks lack. She lacks lack? Curious to put it in so contradictory, so extremely paradoxical, a manner: she lacks lack. To say she lacks lack is also, after all, to say she doesn’t miss lack … since she doesn’t miss the lack of lack. Yes, they say, but the point is “she lacks The Lack,” The Lack, lack of the Phallus. And so, supposedly, she misses the great lack, so that without man she would be indefinite, indefinable, nonsexed, unable to recognize herself: outside the Symbolic. But fortunately there is man: he who comes … Prince Charming. And it’s man who teaches woman (because man is always the Master as well), who teaches her to be aware of lack, to be aware of absence, aware of death. It’s man who will finally order woman, “set her to rights,” by teaching her that without man she could “misrecognize.” He will teach her the Law of the Father. Something of the order of: “Without me, without me-the Absolute-Father (the father is always that much more absolute the more he is improbable, dubious)-without me you wouldn’t exist, I’ll show you.” Without him she’d remain in a state of distressing and distressed undifferentiation, unbordered, unorganized, “unpoliced” by the phallus… incoherent, chaotic, and embedded in the Imaginary in her ignorance of the Law of the Signifier. Without him she would in all probability not be contained by the threat of death, might even, perhaps, believe herself eternal, immortal. Without him she would be deprived of sexuality. And it might be said that man works very actively to produce “his woman.” Take for example Marguerite Duras’ Le Ravissement de Lol V. Stein, and you will witness the moment when man can finally say “his” woman, “my” woman. It is that moment when he has taught her to be aware of Death. So man makes, he makes (up) his woman, not without being himself seized up and drawn into the dialectical movement that this sort of thing sets in play. We might say that the Absolute Woman, in culture, the woman who really represents femininity most effectively… who is closest to femininity as prey to masculinity, is actually the hysteric…. he makes her image for her!
The hysteric is a divine spirit that is always at the edge, the turning point, of making. She is one who does not make herself… she does not make herself but she does make the other. It is said that the hysteric “makes-believe” the father, plays the father, “makes-believe” the master. Plays, makes up, makes-believe: she makes-believe she is a woman, unmakes-believe too … plays at desire, plays the father… turns herself into him, unmakes him at the same time. Anyway, without the hysteric, there’s no father… without the hysteric, no master, no analyst, no analysis! She’s the unorganizable feminine construct, whose power of producing the other is a power that never returns to her. She is really a wellspring nourishing the other for eternity, yet not drawing back from the other … not recognizing herself in the images the other may or may not give her. She is given images that don’t belong to her, and she forces herself, as we’ve all done, to resemble them.
And so in the face of this person who lacks lack, who does not miss lack of lack, we have the construct that is infinitely easier to analyze, to put in place-manhood, flaunting its metaphors like banners through history. You know those metaphors: they are most effective. It’s always clearly a question of war, of battle. If there is no battle, it’s replaced by the stake of battle: strategy. Man is strategy, is reckoning . . . “how to win” with the least possible loss, at the lowest possible cost. Throughout literature masculine figures all say the same thing: “I’m reckoning” what to do to win. Take Don Juan and you have the whole masculine economy getting together to “give women just what it takes to keep them in bed” then swiftly taking back the investment, then reinvesting, etc., so that nothing ever gets given, everything gets taken back, while in the process the greatest possible dividend of pleasure is taken. Consumption without payment, of course.
From Absolutely Live, the first live album released by The Doors in July 1970.
 no one leaves home unless
no one leaves home unless
home is the mouth of a shark
you only run for the border
when you see the whole city running as well
your neighbours running faster than you
breath bloody in their throats
the boy you went to school with
who kissed you dizzy behind the old tin factory
is holding a gun bigger than his body
you only leave home
when home won’t let you stay.
no one leaves home unless home chases you
fire under feet
hot blood in your belly
it’s not something you ever thought of doing
until the blade burnt threats into
your neck
and even then you carried the anthem under
your breath
only tearing up your passport in an airport toilets
sobbing as each mouthful of paper
made it clear that you wouldn’t be going back.
you have to understand,
that no one puts their children in a boat
unless the water is safer than the land
no one burns their palms
under trains
beneath carriages
no one spends days and nights in the stomach of a truck
feeding on newspaper unless the miles travelled
means something more than journey.
no one crawls under fences
no one wants to be beaten
pitied
no one chooses refugee camps
or strip searches where your
body is left aching
or prison,
because prison is safer
than a city of fire
and one prison guard
in the night
is better than a truckload
of men who look like your father
no one could take it
no one could stomach it
no one skin would be tough enough
the
go home blacks
refugees
dirty immigrants
asylum seekers
sucking our country dry
niggers with their hands out
they smell strange
savage
messed up their country and now they want
to mess ours up
how do the words
the dirty looks
roll off your backs
maybe because the blow is softer
than a limb torn off
or the words are more tender
than fourteen men between
your legs
or the insults are easier
to swallow
than rubble
than bone
than your child body
in pieces.
i want to go home,
but home is the mouth of a shark
home is the barrel of the gun
and no one would leave home
unless home chased you to the shore
unless home told you
to quicken your legs
leave your clothes behind
crawl through the desert
wade through the oceans
drown
save
be hunger
beg
forget pride
your survival is more important
no one leaves home until home is a sweaty voice in your ear
saying-
leave,
run away from me now
i dont know what i’ve become
but i know that anywhere
is safer than here
—
Warsan Shire is a Kenyan-born Somali poet, writer and educator based in London. Born in 1988, Warsan has read her work extensively all over Britain and internationally – including recent readings in South Africa, Italy, Germany, Canada, North America and Kenya – and her début book, TEACHING MY MOTHER HOW TO GIVE BIRTH (flipped eye), was published in 2011. Her poems have been published in Wasafiri, Magma and Poetry Review and in the anthology The Salt Book of Younger Poets (Salt, 2011). She is the current poetry editor at SPOOK magazine. In 2012 she represented Somalia at the Poetry Parnassus, the festival of the world poets at the Southbank, London. Warsan is also the unanimous winner of the 2013 Inaugural Brunel University African Poetry Prize.
Rhodes Must Fall issue a powerful new statement:
Here’s a thought piece I wrote for an MPhil African Studies class back in April, in the thick of the Rhodes Must Fall resistance. I want to put it here to archive it.
Problematising the Study Of Africa Assignment:
On Colonial Legacies at the University of Cape Town
—
“Remember that you are an Englishman, and have consequently won first prize in the lottery of life.” — Cecil John Rhodes[1]
“[N]o matter what a white man does, the colour of his skin—his passport to privilege—will always put him miles ahead of the black man. Thus in the ultimate analysis no white person can escape being part of the oppressor camp.” — Bantu Stephen Biko[2]
“For the black man there is only one destiny, and it is white.” — Frantz Fanon[3]
—
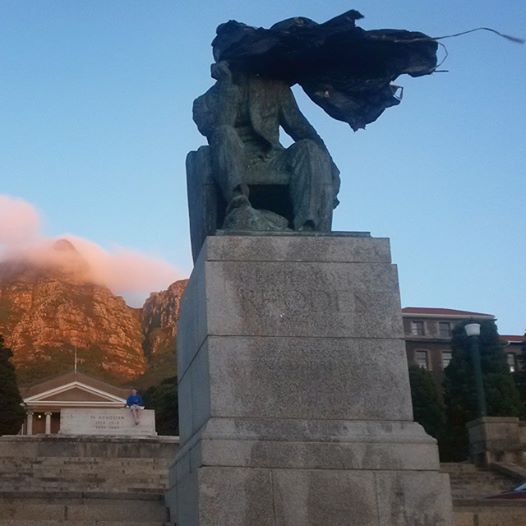

Rhodes statue, head covered in garbage bags. University of Cape Town, 17 March 2015. Photo: Rosemary Lombard
As a child, I remember reading about the railway Cecil John Rhodes envisioned from Cape Town to Cairo, and never imagining it in any light other than as a benevolent feat of engineering that would link people to others, bringing access to resources and the rest of the modern world for those cut off from Western civilisation, literally bringing light to the darkest parts of the continent.
I revised my romantic understanding of Rhodes’ expansionist desires as I became aware of the rampantly exploitative nature of these ambitions, and colonial mechanisms of dominion and exploitation more generally, but it was not until the recent events at UCT surrounding a statue of the man on campus that I realised the true psychological extent and durability of this oppressive colonial legacy, and the way its violence has been rendered almost invisible to those of us on the privileged side of what Walter Mignolo terms the “colonial difference” or divide[4].
The call for transformation is not new: it stretches back more than two decades. The present moment is notable in that students, staff and workers have organised powerfully in concert. A bucket of human excrement thrown on a statue of Rhodes that occupied a central position on UCT’s upper campus escalated tensions around institutional racism that have flared regularly since even before the formal end of the Apartheid era 21 years ago. Black students formed a movement that became known as “Rhodes Must Fall” (RMF) after the social media hashtag they used to mobilise. The students occupied an administrative building for several weeks, in which they held intensive teach-ins and discussions around decolonisation in solidarity with the Students’ Representative Council (SRC), other students, academic staff and workers. University management eventually capitulated to the removal of the statue on 9 April 2015, after a month-long struggle in which RMF demanded to be engaged on their own terms, rather than allowing university management to dictate the terms or to dismiss the protest as had been the case on many previous occasions.
Richard Pithouse describes the mobilisation thus:
The students in Cape Town have, very rapidly, punched a gaping hole into the continuum of English liberal hegemony over the university, and a set of linked sites of a certain kind of elite power, and, thereby, a mode of white supremacy and coloniality that has not been subject to sufficient critique and opposition. It is an extraordinary political achievement that will, no doubt, inscribe itself into the history of the South African academy, and the wider society.[5]
At this historically significant moment, it is on white liberal hegemony and institutional transformation at UCT that I reflect: how has hegemonic whiteness been constructed at UCT, and how does the university continue to function as a colonial space, despite speaking about transformation?
—
I have made several false starts on this assignment (one of which has been losing an entire day’s work on it due to a computer glitch). Initially my idea was to write an open letter to university management, particularly the deputy Vice-Chancellor with the portfolio for transformation, Crain Soudien, whose public behaviour over the past weeks – both in his capacity as a member of university management[6] and in his written statements in the press – has seemed at odds with his historically professed radical stance against uninterrogated hegemony, and his advocacy of deep transformation as chair of the country-wide Ministerial inquiry into institutional racism just a few years ago[7]. Soudien, and other prominent black members of the corporate, academic establishment such as Jonathan Jansen, are interpellated[8] representatives of their institutions’ ideology, and any hint of activism they once displayed has evaporated.
However, I decided that I could not, in good conscience, from my position as an historical beneficiary of the untransformed system, write such a letter. So, dropping the academic apparatus as prompted by this assignment, I feel I have only enough authority to write from a personal, situated angle in attempt to contextualise the recent Rhodes Must Fall chain of events at UCT, with particular reference to the institution’s persisting coloniality. I cannot assume anything other than my own subject position, as a white, cisgender, heterosexual female, who comes from relative privilege. To do so would be disingenuous, as I have learned a trenchant lesson through listening to what students have been saying these past weeks: despite my best intentions and all the empathy I can muster, I cannot have knowledge of what it is to experience institutional racism.
As a “white” person, I have ancestrally been on the powerful side of the racial divide put in place with the advent of Western colonial activity, and I continue to be identified with that subject position. “Whiteness” is the term used to describe the position of privilege this subjectivity puts me and others like me in.
If there is one thing the Rhodes Must Fall moment has driven home to me, it’s that from my subject position I am unqualified to make authoritative pronouncements regarding the experiences or motives of anyone except myself, regardless of racial identity: it’s obvious that I can’t speak to “black” experience, but the most common “white” responses to RMF have largely made me feel alienated, too.
Two decades of rainbow nation narrative have led to the unreflexive “I don’t see colour” rhetoric becoming the status quo among liberal-thinking white South Africans, as well as black people assimilated to corporate institutional capitalist ideology. This is pernicious in that it obscures the very real, material persistence of different life experiences and oppression based on inherited structural inequalities, stemming from racial discrimination.
Coloniality, the set of dispositions, values and forms of practice set in place in the colonial world, outlives the moment of formal political decolonisation, and carries through beyond it in lasting ways. The white Western self speaks from the site of the universal, as a bearer of modernity and civilisation, situated dynamically inside of linear time and at home in a global, cosmopolitan world. All forms of knowledge produced by the Western self, in other words, are deemed to have universal, rational, historical currency.
In contrast, those selves and forms of knowledge encountered by the Western self that are deemed to be other than the Western self are deemed to be “local”, labelled “indigenous”. An indigenous self or indigenous knowledge is constituted as static, standing outside of history and linear time, and inside of tradition, which becomes the opposed category to modernity. Western, colonial knowledge is framed in binaries, in relation to Western supremacy: the privileged poles of these dyads are whiteness, maleness, heterosexuality, and so forth.
Manichean power relationships instituted on the basis of the colonial apparatus did not end with apartheid in 1994. They persist throughout social interactions, their oppressive dynamics all but invisible to those on the privileged side of such relationships, such as white people and males, due to the hegemonic nature of this framing.
A common criticism I saw levelled at black protesters by white commenters was that things changed with the coming of the democratic dispensation in 1994, and that they should stop “holding on to the past” or “playing the race card” with a “victim mentality”, that they should “move on”. But being cognisant of how the legacy of chronologically past events persists into the present is not the same as “holding on to” the past. Only those who are not experiencing the continuation of structural oppression every day can advocate ignoring or disregarding it, and “moving swiftly on”.
Western knowledge systems condition us not to admit any other perspective to the realm of validity. It thus takes concerted effort from white people to listen and not dismiss other points of view if they are to “click” and be able to acknowledge that the hegemonic “white” point of view is not the only, natural point of view. Recognition of the persisting inequality and oppression of black people generates a sense of discomfort and cognitive dissonance. I have realised through conversations with white people I know, as well as the comments I’ve read on social media, that most are unwilling (or perhaps intellectually unable?) to make this effort. Most who identify as liberal (“colour-blind”, non-racist) do not want to accept that they continue to benefit from this system at the expense of others, and display great defensiveness when confronted with the persistence of structural racism, and white complicity therewith.
The comments I have seen by white people who consider themselves liberal and “non-racial” (strenuously disavowing racism) against protesters have been telling – describing them as “uncivilised”, “uneducated”, “unreasonable”, “backward”, “barbarians”, “savages”, “childish”, “monkeys”: these epithets bear the distinctive, unreflexive tang of colonial binaries, binaries set up in implied counterpoint to the opposite values ostensibly possessed by the hallowed university. These colonial tropes have pervaded media, misrepresenting Rhodes Must Fall as an unthinking, destructive mob, when the reality is that the movement created, in a deliberate and considered way, an autonomous space which has surfaced deep pain, but also fostered constructive discussion and reimaginative work.[9]
Acts of physical protest occur when speech has failed, or is perceived to be inadequate. The act of flinging sewage at the statue of Rhodes went beyond talking, because talking was no longer believed to be a viable option for engaging. For dialogue to happen, there needs to be a willingness to listen communicated clearly. UCT, and whiteness more generally, has historically demonstrated itself to be dismissive, unprepared to engage black students’ and staff’s grievances about structural oppression. UCT even went so far as to criminalise protesters.
Steven Friedman remarks:
It is no accident that the protests are happening on the campuses of English-speaking “liberal” universities, which have long claimed to be victims of racism: it is precisely at those institutions that race is kept alive by denying it. Under apartheid, many English-speaking whites insisted that apartheid was created by Afrikaners alone. The “liberal” English-language universities joined in — they proclaimed their right to teach whatever and whomever they pleased, declaring that discrimination was imposed on them by the state. This smugness ignored the extent to which white English speakers in the professions and business profited from the denial of opportunities to others — and the degree to which they believed that blacks could win acceptance only if they adopted the values of whites. The universities ignored the reality that, when they were allowed to do as they pleased, they limited black student numbers and taught courses that assumed that every South African was white… This shows how deep-rooted the attitudes that underpinned apartheid are — and it points a finger at a form of liberalism that has washed its hands of racism while continuing to practise it…
When democracy arrived, the legal barriers tumbled; deep-rooted beliefs that whites are superior did not. The “liberal” universities now had the right to teach who and what they pleased: they used it to keep alive the racial pecking order in a “colour blind” guise… Whites remain largely in charge — but, because they are “liberal”, they always have a good “nonracial” reason for why this should be so.[10]
Hegemonic white power is not always subtle. UCT management has an historical track record of overt institutional racism too. There are several junctures at which these issues have crystallised blatantly, and I will mention two:
In 1968, the accomplished black anthropologist, Archie Mafeje, was made an offer of employment by UCT, but this offer was rescinded under pressure from the Apartheid government, sparking protests. In 1991, the university again offered Mafeje a position. Although he had by that time, 23 years after the first offer, attained the rank of professor, it offered him only a senior lecturer post, still treating him as a junior academic. UCT apologised to Mafeje for this indignity after his death, naming a room in the Bremner building in his honour. It was no coincidence that this room was made the headquarters of Rhodes Must Fall when they occupied that building, renaming it “Azania House” in symbolic redress.
The so-called “Mamdani Affair” unfolded at UCT in 1996 when eminent Ugandan scholar Mahmood Mamdani, who at that point held the AC Jordan Chair in the Centre for African Studies, challenged the university to place African scholarship at the centre of the curriculum. He compiled a curriculum centred on African scholarship which was met with resistance from the all-white advisory committee, apparently because it did not reflect thinkers well-known enough to the committee – that is, it did not reproduce the established western canon of writing about Africa closely enough. Via a manipulation of administrative processes, the curriculum Mamdani planned was rejected and replaced by one produced by the committee. He was suspended and left UCT soon afterwards for the United States. Nomalanga Mkhize charges that the affair “exposed the ignorance of many prominent, predominantly white South African scholars who, because of their racially privileged positions, had risen up the ranks without having to engage three decades of rigorous post-independence African scholarship.”[11]
Black students and academics are angry. Twenty years since the formal end of apartheid, they are still treated as second-class citizens on campus. Only a fraction of teaching staff are black[12], and the syllabus overwhelmingly represents the perspectives of white thinkers. Black thinkers continue to be marginalised. The disciplines are still, overwhelmingly, epistemologically “white”. Francis Nyamnjoh, writing in 2012, describes the insidious outcome of this:
In Africa, the colonial conquest of Africans – body, mind and soul – has led to real or attempted epistemicide – the decimation or near complete killing and replacement of endogenous epistemologies with the epistemological paradigm of the conqueror. The result has been education through schools and other formal institutions of learning in Africa largely as a process of making infinite concessions to the outside – mainly the western world. Such education has tended to emphasize mimicry over creativity, and the idea that little worth learning about, even by Africans, can come from Africa. It champions static dichotomies and boundedness of cultural worlds and knowledge systems. It privileges teleology and analogy over creative negotiation by Africans of the multiple encounters, influences and perspectives evident throughout their continent. It thus impoverishes the complex realities of those it attracts or represses as students.[13]
A statement by UCT’s Student Representative Council, made at a meeting the day the statue was removed, echoes the points made above:
[T]he black folk’s problem is still chiefly the potency of whiteness. In the new democratic dispensation, we have only been concerned with the ‘rainbow nation’ rhetoric and singing kumbaya while our economy still reflects the same socio-economic disparities of the apartheid era. Democracy has granted a few blacks seats at the master’s table; the rest are still fighting over breadcrumbs falling off the table. And it is these few and mostly politically connected ‘privileged’ blacks who assist their white masters in maintaining the status quo.
Whites have not even begun to see blacks as equals and as being capable of thinking for themselves. They continually want to have a say in how we break the shackles of oppression administered and maintained by them. They cry foul as soon as blacks start organising and speaking for themselves. Deep down they understand that they stand to lose their privileges. The white liberal has continued to play a rather peculiar role in the oppression of the black masses, his racist and conservative ways continue to be shielded in his subtle and ‘angelic’ approach. It is the white liberal who is at the forefront of spreading the gospel of integration and a peaceful society. White liberals point towards white conservatives as the problem, and they have convinced themselves that they have arrived at enlightenment pertaining to the sins committed by their forefathers. Yet subconsciously they share the same set of values and desire to protect their privileges.
The ideology and culture of formerly ‘whites only’ spaces has still not changed. What has taken place is that blacks can now access those spaces of learning and living in order to immerse themselves in a western culture. Thus, for the blacks to enjoy the benefits of accessing those places they have to integrate into whiteness. Our integration is nothing but black people assimilating to what is still regarded as righteous, ordained, intelligent, beautiful and angelic whiteness.[14]
Richard Pithouse comments, with hope:
Liberalism has always been fundamentally tied up with the poisonous fantasy of its barbarian other. In 1859 John Stuart Mill, the great philosopher of English liberalism, declared, in his famous essay On Liberty, that “Despotism is a legitimate mode of dealing with barbarians”. The essential logic of actually existing liberalism – freedom for some, despotism for others – was never merely, as they say, academic. In 1887 Rhodes, speaking in parliament in Cape Town echoed these sentiments when he declared that: “we must adopt a system of despotism in our relations with the barbarians of South Africa”.
Yet in 2015, in a society still fundamentally shaped by the historical weight of this idea of freedom for some and despotism for others, a text book for first year politics students, written and prescribed in South African universities, a text book in which not a single African person is presented as a thinker worthy of study, declares that “Most discussions of freedom begin with John Stuart Mill’s On Liberty”.
This sort of academic consensus, which seemed entrenched a few weeks ago, no longer seems to have much of a future. The students have made an intervention of real weight and consequence.
In addressing the necessity of curricular transformation, Harry Garuba writes about the need for a “contrapuntal pedagogy that brings the knowledge of the marginalised to bear on our teaching… The Cecil John Rhodes statue at the centre of the upper campus of UCT may have been physically removed, but what we now need to move is the hegemonic gaze of the Rhodes that is lodged in our ways of thinking… our professional practices as teachers, academics, scholars and students. We need to take a critical look at our everyday routines… In short, we need to remove the Rhodes that lives in our disciplines and the curricula that underpin them.”[15]
—
Stories about the past do not only tell us where we come from. They also tell us where we belong and where we should be headed: they influence how we understand our present and imagine our future. Statues and memorials intentionally inscribe in space particular stories, effectively fixing in stone a version of the past chosen by those in power.
The spatial symbolic order at UCT is hard evidence of the university’s lack of transformation. The university, stretched across the lower slopes of Devil’s Peak, is a carefully curated memorial landscape that concretises colonial ideologies of power and knowledge: a site of prospect, and temple of rarefied knowledge on the hill. Moving through this space as individuals, we are forced to conduct a conversation with these imperial ideas: they exert their influence on us tangibly, directing our attention. Little has been changed about symbolism on the campus in the past twenty years, save for the additive naming of a few buildings and spaces after black icons: Steve Biko Student’s Union, Cissy Gool Plaza, Madiba Circle.
Dependent on one’s subject position, the power exerted by such spatial and ideological configurations feels more or less oppressive. As white people, we may not give much thought to whether we feel at home or belong in the landscape. Black people, on the contrary, constantly confronted by representations of white triumph at the expense of black lives, feel alienated and suffocated. SRC Chair Ramabina Mohapa said at the 16 March meeting convened by UCT management on Heritage Signage and Symbolism, before walking out with most of the student body present, that black students “can no longer breathe”.[16]
As already discussed, colonial dispositions are not easily apprehended or altered, because they remain hegemonic in wider society, rendering them invisible to those who fall on the privileged side of the colonial divide between those privileged and those not privileged.
However, moments in which the symbolic order is ruptured, like the toppling of the Rhodes statue, provide rare opportunities where the usually obscured hegemony becomes plainly apparent. It is at catalytic moments such as these that spacetime is malleable: contrapuntal conversations become possible, competing epistemologies thinkable; candid self-examination and interventions, too. Perhaps substantive transformation happens more effectively in sudden shifts than gradually.
I would like to close with a trio of comments that I gleaned from my Facebook feed on 10 April 2015, the day after Rhodes’ statue was removed.
We stop mistaking Rhodes for a good white person and we stop believing in white supremacy because everywhere you look you see white people’s statues – it’s almost as though there was no one here when they arrived and they just happened to discover the gold (which, coincidentally, was discovered by a black man). When the statues are gone, we can start asking the important questions like why are there 110 white male South African professors and not a single black female South African professor at UCT – South Africa’s most prestigious university. And questions like why is the curriculum at these universities so Eurocentric in its outlook with scant reflection on Africa and her rich history and her bright future. Without these statues and the prestige and honour bestowed on the founding fathers of white supremacy, the leaders of these institutions will have no choice but to answer those questions truthfully and reflect on those answers. Further, removing these reminders of the fallacy of white supremacy leaves space for black excellence to flourish without having to use the white gaze and its tools of measurement to validate itself.
– Fumbatha May
Watched Rhodes fall last night. I’ve never experienced such an atmosphere of happiness and liberation at UCT – particularly when the students refused to let the old bastard go gracefully but crowned him with a bucket of paint as he rode off into the sunset of empire. For the past few weeks, the students have been teaching the university its most important lesson in decades, and will continue to do so for a long time to come. At last, being at UCT is beginning to feel like being at a real university.
– Carlo Germeshuys
Driving home from work passed the plinth where Rhodes stood. It has a tag sprayed on the neat wood box that is covering the base: ‘C.J. WAS HERE ~>’ There is a black girl in a blue dress leaning up on it, smiling broadly as she chats to a white guy in green shorts who is sitting on the edge of it, swinging his legs as he rummages for something in his bookbag beside him. I swear there is a lighter feeling seeing that figure gone! An invitation to a new conversation.
– Debbie Pryor
These comments convey the general mood on campus well: there is a sense of hope and determination that the symbolic fall of Rhodes’ statue will be followed by deep institutional transformation, sentiments I share.
__
REFERENCES
Africa Network Expert Panel. 2014. Why are there so few black professors in South Africa? The Guardian Africa, 6 October 2014. http://www.theguardian.com/world/2014/oct/06/south-africa-race-black-professors
Althusser, L. 1971. “Ideology and Ideological State Apparatuses (Notes towards an Investigation)”. Lenin and Philosophy and Other Essays. Verso.
Biko, S. 1988. I Write What I Like. London: Heinemann.
Friedman, S. 2015. “The racial denialism of South African liberals”. Rand Daily Mail. 1 April 2015. http://www.rdm.co.za/politics/2015/04/01/the-racial-denialism-of-south-african-liberals
Garuba, H. 2015. “What is an African curriculum?” Mail and Guardian, 17 April 2015 00:00. http://mg.co.za/article/2015-04-17-what-is-an-african-curriculum
Goodrich, A. 2015. “Statue controversies in South Africa – reimagine/recontextualise/replace” April 15, 2015. http://www.syntheticzero.net/2015/04/15/statue-controversies-in-south-africa-reimaginerecontextualisereplace/
Majavu, M. 2015. “Uct and Rhodes: Removing Statues, Dismantling Colonial Legacies”. Equal Times, 30 March 2015. http://www.equaltimes.org/uct-and-rhodes-removing-statues?lang=en#.VTUs9tyUd8E
Mangcu, X. 2015. Danger of ‘rationalist conceit’ in Cape Times, March 25 2015 at 01:52pm. http://www.iol.co.za/capetimes/danger-of-rationalist-conceit-1.1836933
Mangcu, X. 2015. “Assault on idea of academic freedom”. Cape Times,April 14 2015 at 01:44pm. http://www.iol.co.za/capetimes/assault-on-idea-of-academic-freedom-1.1844918.
Mignolo, W. 2002. “The Geopolitics of Knowledge and the Colonial Difference”. The South Atlantic Quarterly 101.1 (2002) 57-96. Duke University Press.
Mkhize, N. 2015. “Anger over Rhodes vindicates Mamdani”. Business Day, 7 April 2015. http://www.bdlive.co.za/opinion/columnists/2015/04/07/anger-over-rhodes-vindicates-mamdani
Moodie, A. 2010.”The Soudien Report: Deny racism at your peril”25 April 2010. University World News, Issue No:121. http://www.universityworldnews.com/article.php?story=20100424200305969
Mudimbe, V. 1988. The Invention of Africa: Gnosis, Philosophy and the Order of Knowledge. London: James Curry.
Muller, S. 2014. “Transformation is not UCT’s priority”. Mail and Guardian 21 November 2014. http://mg.co.za/article/2014-11-21-transformation-is-not-ucts-priority
Nyamnjoh, F. 2012. “’Potted Plants in Greenhouses’: A Critical Reflection on the Resilience of Colonial Education in Africa”. Journal of Asian and African Studies. February 15, 2012. doi: 10.1177/0021909611417240.
O’Connell, S & Himmelman, N. 2011. “Lessons in continued oppression: UCT’s conception of post-apartheid freedom sets the bar too low”. https://concernedcasstudents.wordpress.com/2011/05/15/lessons-in-continued-oppression-ucts-conception-of-post-apartheid-freedom-sets-the-bar-too-low/
Pithouse, R. 2015. “South Africa in the Twilight of Liberalism”. Kafila, 19 April 2015. http://kafila.org/2015/04/19/south-africa-in-the-twilight-of-liberalism-richard-pithouse/
Soudien et al. 2008. Report of the Ministerial Committee on Transformation and Social Cohesion and the Elimination of Discrimination in Public Higher Education Institutions. 30 November 2008
Soudien, C. 2015 “UCT stands devoted to debate”. Cape Times, April 14 2015 at 12:43pm. http://www.iol.co.za/capetimes/uct-stands-devoted-to-debate-1.1844882
Wolpe, H. 1995. “The debate on university transformation in South Africa: The case of the University of the Western Cape.” Comparative Education, 31(2): 275 – 292.
___
[1] Attributed in “The lottery of life”, The Independent, 5 May 2001.
[2] From I Write What I Like: Selected Writings by Steve Biko, 1969 – 1972. Heinemann, 1987.
[3] Introduction to Black Skin, White Masks. Translated by Charles Lam Markmann. New York: Grove Press, 1967.
[4] Mignolo, 2002.
[5] Pithouse, 2015.
[6] See, for example, Soudien’s handling of a walkout by the SRC and Rhodes Must Fall during a meeting at UCT on “Heritage, Signage and Symbolism”, 16 March 2015: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4NgpJ00M5Ho
[7] Compare Soudien et al 2008; Alison Moodie’s 2010 interview with Soudien, entitled “The Soudien Report: Deny racism at your peril” and the defensive tone of Soudien 2015.
[8] Althusser, 1971. Interpellation is the process by which the ideology of an institution constitutes individual subjects’ identities through the process of the institution and its discourses ‘hailing’ them in social interactions.
[9] I would like to state as an aside that I do not believe it is the place of beneficiaries of structural racism to offer opinions on how transformation would be best effected. I believe white people should make space to listen and take cues from those who are still being squashed by the non-transformation of the society we inhabit as to what to do. Those who encounter the problem have far more authority in this matter. This is difficult for some white people to grasp due to an ingrained sense of entitlement, and the way whiteness and white knowledge regimes still have hegemonic authority. Several have accused me of promoting self-censorship. It is very far from that. As a white person, to make space for black voices at this moment in the way I am advocating is not to disengage from the debate. It is an active decision to be quiet, to listen and reflect, an action based on a recognition that unless we with white voices behave differently, the status quo of the balance of representation being skewed in the favour of white voices will not change materially.
[10] Friedman, 2015.
[11] Mkhize, 2015.
[12] The number of white professors at UCT stands at about 87 per cent, whereas black professors make up only 4 per cent of the professorial complement (Majavu, 2015).
[13] Nyamnjoh, 2012: 129-130.
[14] UCT SRC statement delivered by Ramabina Mahapa on 9 April 2015. http://www.uct.ac.za/dailynews/?id=9096
[15] Garuba, 2015.
[16] A video of the proceedings can be found at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4NgpJ00M5Ho.
Calling all Europeans… Please sign the petition.
What is the problem?
The EU soon intends to sign two far-reaching trade agreements: one with Canada (CETA = Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement) and one with the USA (TTIP = Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership). The official line is that this will create jobs and increase economic growth. However, the beneficiaries of these agreements are not in fact citizens, but big corporations:
Investor-State-Dispute-Settlement (ISDS): Foreign investors (i.e. Canadian and US companies) receive the right to sue for damages if they believe that they have suffered losses because of laws or measures of the EU or of individual EU member states. This can also affect laws which were enacted in the interest of the common good, such as environmental and consumer protection.
Groups of companies are intended to be included even during the elaboration of new regulations and laws if their trade interests could be affected. The name for this is: “regulatory cooperation”. It means that representatives of big business are invited to participate in expert groups to influence new draft laws, even before these are discussed in the elected parliaments. This undermines democracy!
Big business had, and still has, excessive influence on the secret negotiations relating to CETA and TTIP. Alone in the preparatory phase for TTIP, 590 meetings took place between the EU Commission and lobby representatives, according to official statements. 92% of these meetings were with representatives of companies, while only in a few cases there were discussions with consumer and trade union representatives. And also during the negotiations, representatives of industry are exercising influence. Some formulations in draft texts which have filtered through to the public originate directly from the pens of company lobbyists.
The negotiations are conducted in secret. Even our public representatives know little if anything about their progress. They receive the results in the form of long agreements (the CETA agreement, for example, has about 1,500 pages) only after conclusion of the negotiations, and are therefore able only to either accept or reject the whole agreement without being able to ask for amendments.
Employee rights are coming under pressure, and jobs in numerous industries are endangered. In the USA, only a few basic rights for employees are recognised (only two out of the eight ILO core labour standards). In agriculture and in the electrical industry, massive job losses could occur because of the tougher competition from abroad.
Liberalisation and privatisation are intended to become one-way streets. The return of public utilities, hospitals, or waste collection to the public sector once they have been privatised would be made more difficult or even impossible through CETA and TTIP.
The EU and its member states are falling under pressure to allow risky technologies such as fracking or GM technology.
Foodstuff standards and consumer protection for cosmetics and medical products threaten to be set at the same levels as US standards. However, we need higher rather than lower standards of protection, whether they apply to the use of pesticides, factory farming, or clean sources of energy. Regulatory cooperation and ISDS would make this more difficult or impossible.
CETA and TTIP want to increase the power of multinationals at the expense of democracy and the general good. We must not allow this to happen! Please sign our European Citizens’ Initiative!
Together we can stop TTIP and CETA!
Forever kick-ass, this band. From Mountain Battles (4AD, 2008).
Album: Change of the Century (1960)
Written by Ornette Coleman
Personnel:
Ornette Coleman — alto saxophone
Don Cherry — pocket trumpet
Charlie Haden — bass
Billy Higgins — drums
There’s no such thing as going home
I’m not formed of myself alone
The “human” in the South African context
Whether there is anything which is still to be rediscovered or to be reanimated from the term “the human” takes on a paradoxical resonance in contemporary South Africa. With the end of apartheid, South African culture and society was confronted with the urgency of engaging in affirmative politics in lieu of the politics of destruction of the years of racial segregation. Affirmative politics entailed the production of social horizons of hope. At the same time, it meant resisting both the inertia of the present and the nostalgia of the past. To reconstruct what centuries of racial brutality had destroyed, a balance had to be found between the mobilization, actualization and deployment of cognitive, affective and creative possibilities which had not so far been activated, along with a necessary dose of oppositional consciousness.
Critical humanism in this new context would have meant a persistent commitment to the possibilities and powers of life. There is substantial evidence that a return to the question of the possibilities and powers of life as a precondition for the reconstitution of “the human” in politics and culture was recognized as a matter of ethical and political urgency during the first decade of democracy. During this decade, South Africa became a model of how to dismantle a racial mode of rule, strike down race-based frameworks of citizenship and the law while striving to create racial equality through positive State action. The post-apartheid State fostered a normative project with the aim of achieving justice through reconciliation, equality through economic redress, democracy through the transformation of the law and the restoration of a variety of rights, including the right to a dignified life. This normative project was enshrined in a utopian Constitution that attempts to establish a new relationship between law and society on the one hand and law and life on the other, while equating democracy and the political itself with the ethical and the just. This Constitution’s underlying principle is ubuntu or human mutuality. It promises a transcendence of the old politics of racial difference and an affirmation of a shared humanity. Underpinning the Constitution is the hope that, after centuries of attempts by white power to contain blacks, South Africa could become the speech-act of a certain way of being-in-common rather than side by side.
This drive to “re-humanize” society and culture and to institutionalize a new political community that defines itself as an ethical community is nevertheless unfolding against various odds. Perhaps to a degree hardly achieved in the rest of the Continent, the human has consistently taken on the form of waste within the peculiar trajectory race and capitalism espoused in South Africa. Traditionally, we speak of “waste” as something produced bodily or socially by humans. In this sense, “waste” is that which is other than the human. Traditionally too, we speak of the intrinsic capacity of capitalism to waste human lives. We speak of how workers are wasted under capitalism in comparable fashion to natural resources. Marx in particular characterizes capitalist production as thoroughly wasteful with what he calls “human material” just as it is with “material resources”. It squanders “human beings, living labour”, “squandering not only flesh and blood, but nerves and brain, life and health as well”, he writes. In order to grasp the particular drama of the human in the history of South Africa, we should broaden this traditional definition of “waste” and consider the human itself as a waste product at the interface of race and capitalism. Squandering and wasting black lives has been an intrinsic part of the logic of capitalism, especially in those contexts in which race is central to the simultaneous production of wealth and of superfluous people.
Today, this logic of waste is particularly dramatized by the dilemmas of unemployment and disposability, survival and subsistence, and the expansion in every arena of everyday life of spaces of vulnerability. Despite the emergence of a solid black middle class, a rising superfluous population is becoming a permanent fixture of the South African social landscape with little possibility of ever being exploited by capital. Only a dwindling number of individuals can now claim to be workers in the traditional sense of the term. How to govern the poor has therefore become one of the biggest moral questions facing the nascent democracy. Behind policy debates on “welfare” and “service delivery” loom fundamental ethical choices that will determine the nature of the South African experiment in democracy – questions of how to right historical wrongs; what is the relationship between personal or collective injury and larger problems of equality, justice and the law; hunger and morality; owning and sharing; or even truth, hope and reconciliation. The urgency of these new moral dilemmas is such that, for the democratic project to have any future at all, it should necessarily take the form of a conscious attempt to retrieve life and “the human” from a history of waste.
Wealth and property
Meanwhile, wealth and property have acquired a new salience in public debate. They have become the key, central idioms to framing and naming ongoing social struggles – from imagining the relationship between “the good life” to redefining value itself; from claims of citizenship, rights and entitlements to the definition of the forms of property and the economy itself (whether we should nationalize or not); from matters of morality to those of lifestyle and accountability.
The centrality of wealth in the moral discourse concerning the “human’ is not new. In various parts of pre-colonial Africa, discourses on “the human”, or, on “humanity” almost always took the shape and content of discourses about “wealth”, “personhood” and “social multiplicity”. Traditional definitions of wealth usually encompassed “people”, “things” and “knowledge”.
“People”, that is, other human beings, were not only the most important unit of measurement of ultimate value. They also formed the material basis or infrastructure of human life. ‘People’ consisted of interpersonal dependents of all kinds – wives, children, clients and slaves. As Jane Guyer argues, they were sought, valued, and at times paid for at considerable expense in material terms. Kinship and marriage especially were critical components of accumulative strategies. But wealth also covered traded goods, including the imported goods brought from elsewhere. Things could be personalized objects. Goods could be functionally interchangeable with human beings who in turn could in certain respects be “objectified” or converted into clients or followers.
Wealth – embodied in rights in people – remained a persistent principle of African social and moral life even in the midst of the various shifts induced by the slave trade and colonialism. Knowledge on the other hand was understood as an ever shifting spectrum of possibility. Jane Guyer makes it clear that it was highly valued, complexly organized and plural by definition. There was no social organization of kinship and material life that did not depend, to some extent, on a regime of distribution of knowledge – the arts, music, dance, rhetoric, spiritual life, hunting, gathering, fishing, cultivation, wood-carving, metallurgy. If certain forms of knowledge were specialized, controlled and monopolized by a small cadre of experts or a secret society hierarchy, other forms of knowledge were conceptualized as an open and unbounded repertoire. This unboundedness made it possible for such forms of knowledge to be widely distributed throughout the society and among many adepts on the basis of personal capacity or potentiality.
Indeed, African pre-colonial discourses on the “human” allowed for personal differentiation or singularity. It was believed that certain qualities lived in the individual from his or her birth; which he or she had no need for “magic” to arouse although there was always the indispensable need for magical rites to conserve these. Personal abilities could be augmented, conserved and actualized within the person, making that person a “real person”, recognized as such by the community. Each individual person’s power was itself a composition.
That some of these old tropes might still be at work in current controversies on wealth and property should not be entirely excluded. But that wealth, poverty and property have become essential to the self-understanding of South African society after liberation should also be read against a long history of black dispossession. In the new phase of “frontier accumulation” made possible by the 1994 negotiated settlement, they have become the new idioms for political and normative arguments about what should be the proper relation of people to things; what should be the proper relation of people to each other with respect to things; how much property is enough for one person and how much is too much; how much enjoyment is justifiable especially for the opulent in an environment where hunger and debasement are all too real for many. It is this tension between what looks like an unstoppable logic of unproductive excess on the one hand and on the other, a logic of scarcity and depletion that is turning wealth and property into dramatic sites of contestation.
Wealth and property also operate as means of regulating access to resources that are scarce for some and plentiful for others. They are the main means by which life chances are assigned to different kinds of persons at a time when pockets of wealth and privilege are proving hard not only to account for and even less so to control, but also hard to subject to some form of accountability and redistribution. Furthermore, as Arjun Appadurai observes, the life of the poor has become a strenuous effort to produce, if not a sense of stability, then something like permanence in the face of the temporariness or volatility of almost all the arrangements of social existence. Indeed, one of the most brutal effects of neo-liberalism in South Africa has been the generalization and radicalization of a condition of temporariness for the poor. For many people, the struggle to be alive has taken the form of a struggle against the constant corrosion of the present, both by change and by uncertainty.
In order to reanimate the idea of “the human” in contemporary South African politics and culture, there is therefore no escape from the need to reflect on the thoroughly political and historical character of wealth and property and the extent to which wealth and property have come to be linked with bodily life. If what distinguishes the South African experiment from other such experiments elsewhere in the world is the attempt to establish a new relationship between law and life while equating democracy and the political itself with the ethical and the just, then we have to ask under what conditions can this project of human mutuality result in a broader and more ethical commensality.
Read the rest of this essay HERE.
Brilliant and inspiring lecture by Prof. Achille Mbembe in conversation with Rhodes Must Fall at UCT on 29 April 2015, talking about decolonising the university.
Read his speaking notes here: Achille Mbembe – Decolonizing Knowledge and the Question of the Archive (pdf document).
Charting a path forward for anti-sexist and anti-racist scholarship and activism. This discussion was hosted by the Van Zyl Slabbert Visiting Chair, the Dean of the Faculty of Humanities and the University of Cape Town’s SRC and moderated by Prof Xolela Mangcu on Thursday 23 April 2015.
“The fact that we are able to have this conversation in South Africa as though it is new, as though these issues have never been thought of before, is precisely because of our inability to engage, and to read…In a staggering display of willful ignorance, we continue to have conversations that have been had, that have been taken in remarkable directions, as though we have just discovered them.” – Pumla Gqola (at 0:26:00)
![]() KAFILA - COLLECTIVE EXPLORATIONS SINCE 2006
KAFILA - COLLECTIVE EXPLORATIONS SINCE 2006
[Note: Recent events in South Africa – from raging student movements across university campuses to xenophobic violence in the streets of Durban – seem to echo so many struggles both inside and outside the university “here.” This is the first of hopefully several posts from South Africa, that seek to listen and travel across.]
Guest Post by RICHARD PITHOUSE
South Africa was supposed to be different. We attained our freedom, such as these things are, after everyone else but Palestine. It was late in the day but the afternoon sun was glorious and the best people, people who had passed through the long passage of struggle, told us that we would be able to avoid the mistakes made everywhere else.
There was a mass movement that, whatever its limits, had won tremendous popular support and carried some noble ideals through its travails. Its leaders cast long shadows. Our Constitution, we…
View original post 2,655 more words
Hard-hittin’ straight talk. Brilliant.
“What is worse than the actual racist is all the white folks that set in silence ignoring, denying and dismissing racism, not caring about racism is at the very core of the problem.”
Released on Rough Trade (1983); re-released with this tracklisting in 1993.
In his definitive study of London punk, England’s Dreaming, Jon Savage describes The Raincoats as “rigorously feminist.” While Savage is perhaps the only writer to assign the word rigorous to The Raincoats’ music (a 1980 Village Voice piece contained the line, “The Raincoats say they rehearse”), it is rigorous nonetheless in the way it creates its own aesthetic space and in the way it pursues fun. “They seemed like ordinary people making extraordinary music,” Kim Gordon of Sonic Youth wrote. “Music that was natural that made room for a cohesion of personalities.”
Read more of this biography of the band HERE.