Category Archives: philosophy
john perkins on empire’s power tools
joni mitchell – woman of heart and mind (1972)
Off For The Roses (Asylum Records, 1972).
angela davis and toni morrison on literacy, libraries and liberation (2010)
Recorded at the New York Public Library on October 27, 2010.
the lake #011 – wax junkie – rosemary lombard – september 2016
“I’m an insatiable explorer. I’ll find music via any route I can, but vinyl is my favourite medium for its wonderful tactility. I’ve been collecting records since I was about 14. My pocket money didn’t stretch to buying CDs regularly, so I turned to second-hand LPs because I could buy speculatively and get a rush of novelty for R2 or R5 a pop. Every great record holds a slice of adventure – as it spins, thin air is transformed by sound into a tangible place you inhabit. You can take listeners anywhere your imagination and collection will stretch, and I think this can really expand your capacity for empathy.”
Read it in The Lake, and listen below.
Kate Bush – Hounds of Love/The Ninth Wave (EMI, 1985)
Choosing only six records to feature here was an ordeal because the span of what has shaped me is just so wide. I decided to restrict contenders to female artists, who are often under-represented in these kinds of list. I got down to about 20 possibilities but then had to shuffle and pick randomly with my eyes closed. So, for starters, what’s there to say that hasn’t already been said about the brilliance of Kate Bush? This album is a perennial go-to for me on grey, melancholy-drenched days – the second side, beginning with “And Dream of Sheep”, in particular. It’s also something of a litmus test. I’ve realised over the years that if someone new I meet loves this record deeply, it’s almost a given that we’re going to click alchemically.
___
Nina Simone – Little Girl Blue (Bethlehem, 1958)
This was Nina Simone’s first album, recorded when she was just 25. Despite her youth, her mastery of expression is already consummate here. I often listen to music medicinally, and this is one of those records I turn to when I’m really over the world in general. Nina’s voice and piano carry all the bittersweet weight of living. “All you can ever count on are the raindrops…” The notes spill out exquisitely, painting cathedrals where my spirit can shelter, smoky bars where my soul can dance. Any morning I’m struggling to pull myself together, if I drop the needle on “Good Bait”, by the time it’s resolutely swinging, two minutes in, the kettle will be on the boil and I’ll be thinking of what to wear.
___
Sathima Bea Benjamin – Windsong (Ekapa, 1985)
Windsong was recorded in New York in June 1985 and released on Ekapa RPM, the label launched by Sathima in 1979 to publish her own music and that of her then-husband Abdullah Ibrahim. A meditation on exile, displacement and yearning, the album opens with a haunting rendition of “Sometimes I Feel like a Motherless Child”, alongside Sathima’s own compositions. Windsong is dedicated to “the resilient, remarkable, and courageous mothers and daughters of the struggle for peace and liberation in my homeland, South Africa, to the heroines both sung and unsung”. My copy is extra precious to me because Sathima signed it for me just a couple of weeks before she passed away in 2013.
___
Forces Favourites – Eleven Songs by South Africans Supporting the End Conscription Campaign (Shifty Records/Rounder Records, 1986)
This compilation was released by legendary South African label Shifty Records in support of the movement for conscientious objectors against compulsory military service in the apartheid army. Jennifer Ferguson’s chillingly honest exploration of white privilege and paranoia, “Suburban Hum”, still feels relevant right now. It’s a highlight on this record for me, along with “Shot Down” by James Phillips’s Cherry-Faced Lurchers and the Kalahari Surfers’ “Don’t Dance”. I’ve owned the South African release for a long time, but last year, while living in a small university town in Sweden for a semester, I also picked up a US pressing with a different cover. While there, I was also privileged to meet Jennifer herself. She happens to live in the very same town, and is doing inspiring creative work with refugees.
___
Julia Holter – Ekstasis (Rvng Intl., 2012)
Los Angeles-based composer Julia Holter makes music which is conceptually dense, yet spacious and eminently listenable – hummable even. I saw her give a phenomenal performance last year in Stockholm. I already had three of her albums on mp3, including Ekstasis, so that night I grabbed this, which the merch guy told me was one of the last copies of the out-of-print 12” 45rpm double vinyl release. By drawing on archetypes from Greek tragedy, this album simultaneously abstracts personal narrative and renders the emotional content conveyed universal. It’s a clever conceit, but one you don’t need to be aware of in order to appreciate the music. An obvious comparison to draw would be with the work of Laurie Anderson (whose ground-breaking 1982 debut, Big Science, was also on my shortlist for this article).
___
The Raincoats – Odyshape (Rough Trade, 1981)
I read somewhere that following the release of their eponymous first album in 1979, the Raincoats were one of the first bands to be called “post-punk”. John Lydon said they were the best band in the world. Kurt Cobain wrote the liner notes for their first album’s 1993 re-release. None of this hype really prepares one for the shambolic assemblage of punk, folk and lo-fi that is the Raincoats’ second album, Odyshape, though. A wildly experimental departure into unmapped territory, the melodies float loosely over an assortment of unusually textured percussive instruments, including kalimba and balafon. This record still sounds extraordinary 35 years on: intimate and vulnerable, uncompromisingly feminine. I can definitely hear its influence on later artists such as Micachu and the Shapes, and Tune-Yards.
___
This profile was published HERE.
hélène cixous on the term “intellectual” and other problematic words (1992)
bell hooks – understanding patriarchy (2004)
“The crisis facing men is not the crisis of masculinity, it is the crisis of patriarchal masculinity. Until we make this distinction clear, men will continue to fear that any critique of patriarchy represents a threat.”
Patriarchy is the single most life-threatening social disease assaulting the male body and spirit in our nation. Yet most men do not use the word “patriarchy” in everyday life. Most men never think about patriarchy—what it means, how it is created and sustained. Many men in our nation would not be able to spell the word or pronounce it correctly. The word “patriarchy” just is not a part of their normal everyday thought or speech.
Men who have heard and know the word usually associate it with women’s liberation, with feminism, and therefore dismiss it as irrelevant to their own experiences. I have been standing at podiums talking about patriarchy for more than thirty years. It is a word I use daily, and men who hear me use it often ask me what I mean by it.
Nothing discounts the old antifeminist projection of men as all-powerful more than their basic ignorance of a major facet of the political system that shapes and informs male identity and sense of self from birth until death. I often use the phrase “imperialist white-supremacist capitalist patriarchy” to describe the interlocking political systems that are the foundation of our nation’s politics. Of these systems the one that we all learn the most about growing up is the system of patriarchy, even if we never know the word, because patriarchal gender roles are assigned to us as children and we are given continual guidance about the ways we can best fulfill these roles.
Patriarchy is a political-social system that insists that males are inherently dominating, superior to everything and everyone deemed weak, especially females, and endowed with the right to dominate and rule over the weak and to maintain that dominance through various forms of psychological terrorism and violence. When my older brother and I were born with a year separating us in age, patriarchy determined how we would each be regarded by our parents. Both our parents believed in patriarchy; they had been taught patriarchal thinking through religion.
At church they had learned that God created man to rule the world and everything in it and that it was the work of women to help men perform these tasks, to obey, and to always assume a subordinate role in relation to a powerful man. They were taught that God was male. These teachings were reinforced in every institution they encountered– schools, courthouses, clubs, sports arenas, as well as churches. Embracing patriarchal thinking, like everyone else around them, they taught it to their children because it seemed like a “natural” way to organize life.
As their daughter I was taught that it was my role to serve, to be weak, to be free from the burden of thinking, to caretake and nurture others. My brother was taught that it was his role to be served; to provide; to be strong; to think, strategize, and plan; and to refuse to caretake or nurture others. I was taught that it was not proper for a female to be violent, that it was “unnatural.” My brother was taught that his value would be determined by his will to do violence (albeit in appropriate settings). He was taught that for a boy, enjoying violence was a good thing (albeit in appropriate settings). He was taught that a boy should not express feelings. I was taught that girls could and should express feelings, or at least some of them.
When I responded with rage at being denied a toy, I was taught as a girl in a patriarchal household that rage was not an appropriate feminine feeling, that it should not only not be expressed but be eradicated. When my brother responded with rage at being denied a toy, he was taught as a boy in a patriarchal household that his ability to express rage was good but that he had to learn the best setting to unleash his hostility. It was not good for him to use his rage to oppose the wishes of his parents, but later, when he grew up, he was taught that rage was permitted and that allowing rage to provoke him to violence would help him protect home and nation.
We lived in farm country, isolated from other people. Our sense of gender roles was learned from our parents, from the ways we saw them behave. My brother and I remember our confusion about gender. In reality I was stronger and more violent than my brother, which we learned quickly was bad. And he was a gentle, peaceful boy, which we learned was really bad. Although we were often confused, we knew one fact for certain: we could not be and act the way we wanted to, doing what we felt like. It was clear to us that our behavior had to follow a predetermined, gendered script. We both learned the word “patriarchy” in our adult life, when we learned that the script that had determined what we should be, the identities we should make, was based on patriarchal values and beliefs about gender.
I was always more interested in challenging patriarchy than my brother was because it was the system that was always leaving me out of things that I wanted to be part of. In our family life of the fifties, marbles were a boy’s game. My brother had inherited his marbles from men in the family; he had a tin box to keep them in. All sizes and shapes, marvelously colored, they were to my eye the most beautiful objects. We played together with them, often with me aggressively clinging to the marble I liked best, refusing to share. When Dad was at work, our stay-at-home mom was quite content to see us playing marbles together. Yet Dad, looking at our play from a patriarchal perspective, was disturbed by what he saw. His daughter, aggressive and competitive, was a better player than his son. His son was passive; the boy did not really seem to care who won and was willing to give over marbles on demand. Dad decided that this play had to end, that both my brother and I needed to learn a lesson about appropriate gender roles.
One evening my brother was given permission by Dad to bring out the tin of marbles. I announced my desire to play and was told by my brother that “girls did not play with marbles,” that it was a boy’s game. This made no sense to my four- or five-year-old mind, and I insisted on my right to play by picking up marbles and shooting them. Dad intervened to tell me to stop. I did not listen. His voice grew louder and louder. Then suddenly he snatched me up, broke a board from our screen door, and began to beat me with it, telling me, “You’re just a little girl. When I tell you to do something, I mean for you to do it.” He beat me and he beat me, wanting me to acknowledge that I understood what I had done. His rage, his violence captured everyone’s attention. Our family sat spellbound, rapt before the pornography of patriarchal violence.
After this beating I was banished—forced to stay alone in the dark. Mama came into the bedroom to soothe the pain, telling me in her soft southern voice, “I tried to warn you. You need to accept that you are just a little girl and girls can’t do what boys do.” In service to patriarchy her task was to reinforce that Dad had done the right thing by, putting me in my place, by restoring the natural social order.
I remember this traumatic event so well because it was a story told again and again within our family. No one cared that the constant retelling might trigger post-traumatic stress; the retelling was necessary to reinforce both the message and the remembered state of absolute powerlessness. The recollection of this brutal whipping of a little-girl daughter by a big strong man, served as more than just a reminder to me of my gendered place, it was a reminder to everyone watching/remembering, to all my siblings, male and female, and to our grown-woman mother that our patriarchal father was the ruler in our household. We were to remember that if we did not obey his rules, we would be punished, punished even unto death. This is the way we were experientially schooled in the art of patriarchy.
There is nothing unique or even exceptional about this experience. Listen to the voices of wounded grown children raised in patriarchal homes and you will hear different versions with the same underlying theme, the use of violence to reinforce our indoctrination and acceptance of patriarchy. In How Can I Get Through to You? family therapist Terrence Real tells how his sons were initiated into patriarchal thinking even as their parents worked to create a loving home in which antipatriarchal values prevailed. He tells of how his young son Alexander enjoyed dressing as Barbie until boys playing with his older brother witnessed his Barbie persona and let him know by their gaze and their shocked, disapproving silence that his behavior was unacceptable:
Without a shred of malevolence, the stare my son received transmitted a message. You are not to do this. And the medium that message was broadcast in was a potent emotion: shame. At three, Alexander was learning the rules. A ten second wordless transaction was powerful enough to dissuade my son from that instant forward from what had been a favorite activity. I call such moments of induction the “normal traumatization” of boys.
To indoctrinate boys into the rules of patriarchy, we force them to feel pain and to deny their feelings.
My stories took place in the fifties; the stories Real tells are recent. They all underscore the tyranny of patriarchal thinking, the power of patriarchal culture to hold us captive. Real is one of the most enlightened thinkers on the subject of patriarchal masculinity in our nation, and yet he lets readers know that he is not able to keep his boys out of patriarchy’s reach. They suffer its assaults, as do all boys and girls, to a greater or lesser degree. No doubt by creating a loving home that is not patriarchal, Real at least offers his boys a choice: they can choose to be themselves or they can choose conformity with patriarchal roles. Real uses the phrase “psychological patriarchy” to describe the patriarchal thinking common to females and males. Despite the contemporary visionary feminist thinking that makes clear that a patriarchal thinker need not be a male, most folks continue to see men as the problem of patriarchy. This is simply not the case. Women can be as wedded to patriarchal thinking and action as men.
Psychotherapist John Bradshaw’s clear sighted definition of patriarchy in Creating Love is a useful one: “The dictionary defines ‘patriarchy’ as a ‘social organization marked by the supremacy of the father in the clan or family in both domestic and religious functions’.” Patriarchy is characterized by male domination and power. He states further that “patriarchal rules still govern most of the world’s religious, school systems, and family systems.” Describing the most damaging of these rules, Bradshaw lists “blind obedience—the foundation upon which patriarchy stands; the repression of all emotions except fear; the destruction of individual willpower; and the repression of thinking whenever it departs from the authority figure’s way of thinking.” Patriarchal thinking shapes the values of our culture. We are socialized into this system, females as well as males. Most of us learned patriarchal attitudes in our family of origin, and they were usually taught to us by our mothers. These attitudes were reinforced in schools and religious institutions.
The contemporary presence of female-headed households has led many people to assume that children in these households are not learning patriarchal values because no male is present. They assume that men are the sole teachers of patriarchal thinking. Yet many female-headed households endorse and promote patriarchal thinking with far greater passion than two-parent households. Because they do not have an experiential reality to challenge false fantasies of gender roles, women in such households are far more likely to idealize the patriarchal male role and patriarchal men than are women who live with patriarchal men every day. We need to highlight the role women play in perpetuating and sustaining patriarchal culture so that we will recognize patriarchy as a system women and men support equally, even if men receive more rewards from that system. Dismantling and changing patriarchal culture is work that men and women must do together.
Clearly we cannot dismantle a system as long as we engage in collective denial about its impact on our lives. Patriarchy requires male dominance by any means necessary, hence it supports, promotes, and condones sexist violence. We hear the most about sexist violence in public discourses about rape and abuse by domestic partners. But the most common forms of patriarchal violence are those that take place in the home between patriarchal parents and children. The point of such violence is usually to reinforce a dominator model, in which the authority figure is deemed ruler over those without power and given the right to maintain that rule through practices of subjugation, subordination, and submission.
Keeping males and females from telling the truth about what happens to them in families is one way patriarchal culture is maintained. A great majority of individuals enforce an unspoken rule in the culture as a whole that demands we keep the secrets of patriarchy, thereby protecting the rule of the father. This rule of silence is upheld when the culture refuses everyone easy access even to the word “patriarchy.” Most children do not learn what to call this system of institutionalized gender roles, so rarely do we name it in everyday speech. This silence promotes denial. And how can we organize to challenge and change a system that cannot be named?
It is no accident that feminists began to use the word “patriarchy” to replace the more commonly used “male chauvinism” and “sexism.” These courageous voices wanted men and women to become more aware of the way patriarchy affects us all. In popular culture the word itself was hardly used during the heyday of contemporary feminism. Antimale activists were no more eager than their sexist male counterparts to emphasize the system of patriarchy and the way it works. For to do so would have automatically exposed the notion that men were all-powerful and women powerless, that all men were oppressive and women always and only victims. By placing the blame for the perpetuation of sexism solely on men, these women could maintain their own allegiance to patriarchy, their own lust for power. They masked their longing to be dominators by taking on the mantle of victimhood.
Like many visionary radical feminists I challenged the misguided notion, put forward by women who were simply fed up with male exploitation and oppression, that men were “the enemy.” As early as 1984 I included a chapter with the title “Men: Comrades in Struggle” in my book Feminist Theory: From Margin to Center urging advocates of feminist politics to challenge any rhetoric which placed the sole blame for perpetuating patriarchy and male domination onto men:
Separatist ideology encourages women to ignore the negative impact of sexism on male personhood. It stresses polarization between the sexes. According to Joy Justice, separatists believe that there are “two basic perspectives” on the issue of naming the victims of sexism: “There is the perspective that men oppress women. And there is the perspective that people are people, and we are all hurt by rigid sex roles.”…Both perspectives accurately describe our predicament. Men do oppress women. People are hurt by rigid sexist role patterns, These two realities coexist. Male oppression of women cannot be excused by the recognition that there are ways men are hurt by rigid sexist roles. Feminist activists should acknowledge that hurt, and work to change it—it exists. It does not erase or lessen male responsibility for supporting and perpetuating their power under patriarchy to exploit and oppress women in a manner far more grievous than the serious psychological stress and emotional pain caused by male conformity to rigid sexist role patterns.
Throughout this essay I stressed that feminist advocates collude in the pain of men wounded by patriarchy when they falsely represent men as always and only powerful, as always and only gaining privileges from their blind obedience to patriarchy. I emphasized that patriarchal ideology brainwashes men to believe that their domination of women is beneficial when it is not:
Often feminist activists affirm this logic when we should be constantly naming these acts as expressions of perverted power relations, general lack of control of one’s actions, emotional powerlessness, extreme irrationality, and in many cases, outright insanity. Passive male absorption of sexist ideology enables men to falsely interpret this disturbed behavior positively. As long as men are brainwashed to equate violent domination and abuse of women with privilege, they will have no understanding of the damage done to themselves or to others, and no motivation to change.
Patriarchy demands of men that they become and remain emotional cripples. Since it is a system that denies men full access to their freedom of will, it is difficult for any man of any class to rebel against patriarchy, to be disloyal to the patriarchal parent, be that parent female or male.
The man who has been my primary bond for more than twelve years was traumatized by the patriarchal dynamics in his family of origin. When I met him he was in his twenties. While his formative years had been spent in the company of a violent, alcoholic dad, his circumstances changed when he was twelve and he began to live alone with his mother.
In the early years of our relationship he talked openly about his hostility and rage toward his abusing dad. He was not interested in forgiving him or understanding the circumstances that had shaped and influenced his dad’s life, either in his childhood or in his working life as a military man. In the early years of our relationship he was extremely critical of male domination of women and children. Although he did not use the word “patriarchy,” he understood its meaning and he opposed it. His gentle, quiet manner often led folks to ignore him, counting him among the weak and the powerless. By the age of thirty he began to assume a more macho persona, embracing the dominator model that he had once critiqued. Donning the mantle of patriarch, he gained greater respect and visibility. More women were drawn to him. He was noticed more in public spheres. His criticism of male domination ceased. And indeed he begin to mouth patriarchal rhetoric, saying the kind of sexist stuff that would have appalled him in the past.
These changes in his thinking and behavior were triggered by his desire to be accepted and affirmed in a patriarchal workplace and rationalized by his desire to get ahead. His story is not unusual. Boys brutalized and victimized by patriarchy more often than not become patriarchal, embodying the abusive patriarchal masculinity that they once clearly recognized as evil. Few men brutally abused as boys in the name of patriarchal maleness courageously resist the brainwashing and remain true to themselves. Most males conform to patriarchy in one way or another.
Indeed, radical feminist critique of patriarchy has practically been silenced in our culture. It has become a subcultural discourse available only to well-educated elites. Even in those circles, using the word “patriarchy” is regarded as passé. Often in my lectures when I use the phrase “imperialist white-supremacist capitalist patriarchy” to describe our nation’s political system, audiences laugh. No one has ever explained why accurately naming this system is funny. The laughter is itself a weapon of patriarchal terrorism. It functions as a disclaimer, discounting the significance of what is being named. It suggests that the words themselves are problematic and not the system they describe. I interpret this laughter as the audience’s way of showing discomfort with being asked to ally themselves with an anti-patriarchal disobedient critique. This laughter reminds me that if I dare to challenge patriarchy openly, I risk not being taken seriously.
Citizens in this nation fear challenging patriarchy even as they lack overt awareness that they are fearful, so deeply embedded in our collective unconscious are the rules of patriarchy. I often tell audiences that if we were to go door-to-door asking if we should end male violence against women, most people would give their unequivocal support. Then if you told them we can only stop male violence against women by ending male domination, by eradicating patriarchy, they would begin to hesitate, to change their position. Despite the many gains of contemporary feminist movement—greater equality for women in the workforce, more tolerance for the relinquishing of rigid gender roles—patriarchy as a system remains intact, and many people continue to believe that it is needed if humans are to survive as a species. This belief seems ironic, given that patriarchal methods of organizing nations, especially the insistence on violence as a means of social control, has actually led to the slaughter of millions of people on the planet.
Until we can collectively acknowledge the damage patriarchy causes and the suffering it creates, we cannot address male pain. We cannot demand for men the right to be whole, to be givers and sustainers of life. Obviously some patriarchal men are reliable and even benevolent caretakers and providers, but still they are imprisoned by a system that undermines their mental health.
Patriarchy promotes insanity. It is at the root of the psychological ills troubling men in our nation. Nevertheless there is no mass concern for the plight of men. In Stiffed: The Betrayal of the American Man, Susan Faludi includes very little discussion of patriarchy:
Ask feminists to diagnose men’s problems and you will often get a very clear explanation: men are in crisis because women are properly challenging male dominance. Women are asking men to share the public reins and men can’t bear it. Ask antifeminists and you will get a diagnosis that is, in one respect, similar. Men are troubled, many conservative pundits say, because women have gone far beyond their demands for equal treatment and are now trying to take power and control away from men…The underlying message: men cannot be men, only eunuchs, if they are not in control. Both the feminist and antifeminist views are rooted in a peculiarly modern American perception that to be a man means to be at the controls and at all times to feel yourself in control.
Faludi never interrogates the notion of control. She never considers that the notion that men were somehow in control, in power, and satisfied with their lives before contemporary feminist movement is false.
Patriarchy as a system has denied males access to full emotional well-being, which is not the same as feeling rewarded, successful, or powerful because of one’s capacity to assert control over others. To truly address male pain and male crisis we must as a nation be willing to expose the harsh reality that patriarchy has damaged men in the past and continues to damage them in the present. If patriarchy were truly rewarding to men, the violence and addiction in family life that is so all-pervasive would not exist. This violence was not created by feminism. If patriarchy were rewarding, the overwhelming dissatisfaction most men feel in their work lives—a dissatisfaction extensively documented in the work of Studs Terkel and echoed in Faludi’s treatise—would not exist.
In many ways Stiffed was yet another betrayal of American men because Faludi spends so much time trying not to challenge patriarchy that she fails to highlight the necessity of ending patriarchy if we are to liberate men. Rather she writes:
Instead of wondering why men resist women’s struggle for a freer and healthier life, I began to wonder why men refrain from engaging in their own struggle. Why, despite a crescendo of random tantrums, have they offered no methodical, reasoned response to their predicament: Given the untenable and insulting nature of the demands placed on men to prove themselves in our culture, why don’t men revolt?…Why haven’t men responded to the series of betrayals in their own lives—to the failures of their fathers to make good on their promises–with something coequal to feminism?
Note that Faludi does not dare risk either the ire of feminist females by suggesting that men can find salvation in feminist movement or rejection by potential male readers who are solidly antifeminist by suggesting that they have something to gain from engaging feminism. So far in our nation visionary feminist movement is the only struggle for justice that emphasizes the need to end patriarchy. No mass body of women has challenged patriarchy and neither has any group of men come together to lead the struggle. The crisis facing men is not the crisis of masculinity, it is the crisis of patriarchal masculinity. Until we make this distinction clear, men will continue to fear that any critique of patriarchy represents a threat. Distinguishing political patriarchy, which he sees as largely committed to ending sexism, therapist Terrence Real makes clear that the patriarchy damaging us all is embedded in our psyches: Psychological patriarchy is the dynamic between those qualities deemed “masculine” and “feminine” in which half of our human traits are exalted while the other half is devalued. Both men and women participate in this tortured value system.
Psychological patriarchy is a “dance of contempt,” a perverse form of connection that replaces true intimacy with complex, covert layers of dominance and submission, collusion and manipulation. It is the unacknowledged paradigm of relationships that has suffused Western civilization generation after generation, deforming both sexes, and destroying the passionate bond between them.
By highlighting psychological patriarchy, we see that everyone is implicated and we are freed from the misperception that men are the enemy. To end patriarchy we must challenge both its psychological and its concrete manifestations in daily life. There are folks who are able to critique patriarchy but unable to act in an antipatriarchal manner.
To end male pain, to respond effectively to male crisis, we have to name the problem. We have to both acknowledge that the problem is patriarchy and work to end patriarchy. Terrence Real offers this valuable insight:
“The reclamation of wholeness is a process even more fraught for men than it has been for women, more difficult and more profoundly threatening to the culture at large.”
If men are to reclaim the essential goodness of male being, if they are to regain the space of openheartedness and emotional expressiveness that is the foundation of well-being, we must envision alternatives to patriarchal masculinity. We must all change.
___
This is an excerpt from The Will To Change by bell hooks (chapter 2).
bell hooks is an American social activist, feminist and author. She was born on September 25, 1952. bell hooks is the nom de plume for Gloria Jean Watkins. bell hooks examines the multiple networks that connect gender, race, and class. She examines systematic oppression with the goal of a liberatory politics. She also writes on the topics of mass media, art, and history. bell hooks is a prolific writer, having composed a plethora of articles for mainstream and scholarly publications. bell hooks has written and published dozens of books. At Yale University, bell hooks was a Professor of African and African-American Studies and English. At Oberlin College, she was an Associate Professor of Women‚’s Studies and American Literature. At the City College of New York, bell hooks also held the position of Distinguished Lecturer of English Literature. bell hooks has been awarded The American Book Awards/Before Columbus Foundation Award, The Writer’s Award from Lila Wallace-Reader’s Digest Fund, and The Bank Street College Children’s Book of the Year. She has also been ranked as one of the most influential American thinkers by Publisher’s Weekly and The Atlantic monthly.
This work is licensed under an Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
tim hjersted on what we are here for
I have made a promise to this world that I will carry with me to my last days. It is my vow to lessen the suffering of the world while I am here – it is to ensure that every toxic legacy that I inherited from our culture ends with me – and, ideally, ends with all of us, in our lifetime. The task may be impossible, but I have to help. I have to do it because my true nature wants me to. When I do this work, my heart sings. My inner self rejoices. That is because your happiness is my happiness. Doing the work connects me with what is really true. We are all connected. We are all in relationship.
Focusing on media activism, it is quite easy to get swept up in a thousand different messages, leaving me sometimes feeling like I’ve gotten off track with my core message and purpose. What am I doing here? Why am I here?
The answer is in an old Sufi song I learned as a child, “What are we here for? To love, serve and remember.”
To love, serve and remember.
Remember what?
That we are all family.
That you are because I am.
That what is sacred in me is sacred in you. And that sacredness pervades the cosmos, if we choose.*
Reverence and awe for the world is our choice to make. We can see that beauty, and live that life, or we can choose not to see it, and live without that beauty.
Look at your lover this way today. See the sacred in her. See the sacred in him. When you see it in them, see it in your family and your friends. Then, start looking for it in people you see at the grocery store and on the street. Then see it in all of the animal creatures in your life. See it in the trees and plants that grow outside your house. See life in everything, truly be present to its nature and vibrational energy.
Each person in the world is family – caught with us amid the “splendour and travail of the earth.”
When we see the sacred in every person, we can see that those who cause others to suffer are also suffering and have been deeply wounded by this culture since they were born. Every child is born with love in their hearts. The child does not know that we are not all family until they are taught so. This is how we forget.
Our culture teaches us to forget. Our culture teaches us who to love and who not to love. It is a very small circle of people. But that circle is growing bigger for more and more people each day.
More and more people are remembering that our family is life itself.
That is the core message I am trying to spread with my activism.
From this revolution of the heart flowers every other revolution. Sexism, racism, environmental destruction, poverty and war are not possible when true love is there. True love dissolves illusion. True love shatters prejudice and malice. True love liberates both the child and the adult from centuries of our inherited suffering. It is the revolution we need most desperately to save every 5 year old child from the suffering they will inherit if we do not vow to ensure that every toxic cultural legacy of our culture ends with us.
*I define sacred as something having intrinsic worth and value, so for me the word connects with me on both a secular and spiritual level. In a scientific sense that value may be entirely subjective, but I’m okay with that. For me, it’s a choice to see the sacred in life. I can choose to see that beauty, or not see it.
___
Tim Hjersted is the director and co-founder of Films For Action. 16 August 2016.
This work is licensed under an Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
“bared life” – looking at stereographs of south african miners produced in the early 1900s (rosemary lombard, 2014)
This is a research paper I wrote in 2014 for “The Public Life of the Image”, an MPhil course offered through the Centre for African Studies at the University of Cape Town.
“[T]he striking mine workers at Marikana have become spectacularised. It is a stark reminder that the mine worker, a modern subject of capitalism, in these parts of the world is also the product of a colonial encounter.”
— Suren Pillay (2014)
“We need to understand how photography works within everyday life in advanced industrial societies: the problem is one of materialist cultural history rather than art history.”
— Allan Sekula (2003)
__
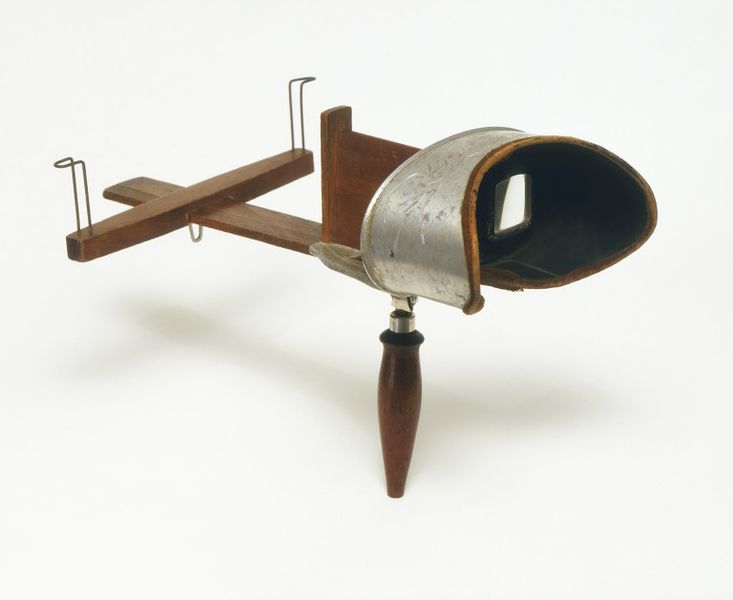
I pick up the odd wood and metal contraption. This is a stereoscope, I am told. It feels old, in the sense that there is a certain worn patina about it, and a non-utilitarian elegance to the turned wood and decoration, though not as if it were an expensive piece – just as if it came from an era where there was time for embellishment. It feels cheaply put together, mass-produced and flimsy as opposed to delicate, the engraving detail of the tinny sheet metal rather rough, the fit of the one piece as it glides through the other somewhat rickety in my hands.
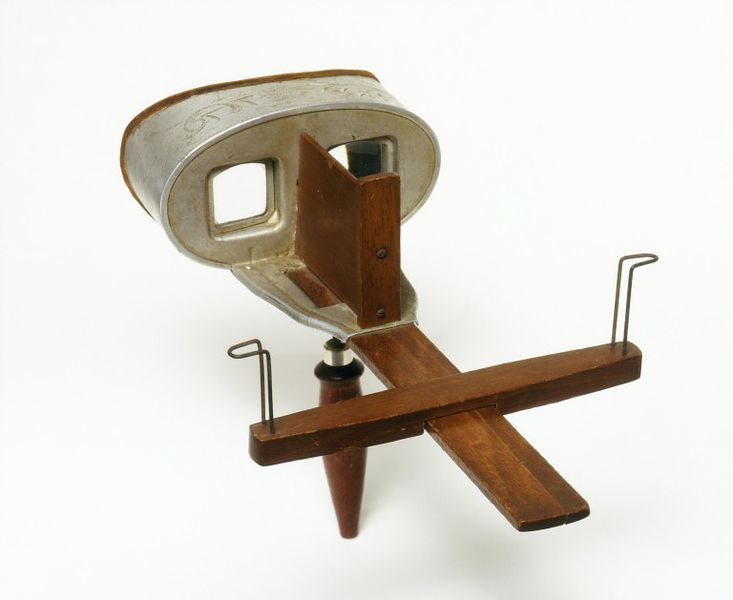

From two elevations, a stereoscope almost identical to the one I used. Various kinds were devised in the 19th century. The particular hand-held variety, of oak, tin, glass and velvet depicted here dates back to 1901, Based on a design by the inventor Oliver Wendell Holmes, it is perhaps the most readily available and simplest model.
I reach for the pile of faded stereographs; flipping through them slowly. There are 24, picked up in an antique shop in an arcade off Cape Town’s Long Street together with the viewing device. A stereograph is composed of two photographs of the same subject taken from slightly different angles. When placed in the stereoscope’s wire holder, and viewed through the eyeholes, an illusion of perspective and depth is achieved as the two images appear to combine through a trick of parallax.
Susan Sontag remarks that “[p]hotographs, which cannot themselves explain anything, are inexhaustible invitations to deduction, speculation, and fantasy”2. And Allan Sekula calls the photograph an “incomplete utterance, a message that depends on some external matrix of conditions and presuppositions for its readability. That is, the meaning of any photographic message is necessarily context determined”3. In what follows, while unable to offer definitive conclusions, I will look more closely at 2 out of these 24 pictures and, through a contextual discussion, attempt to unpack a few aspects of the complex relationships of photography with its subjects and also with public circulation.
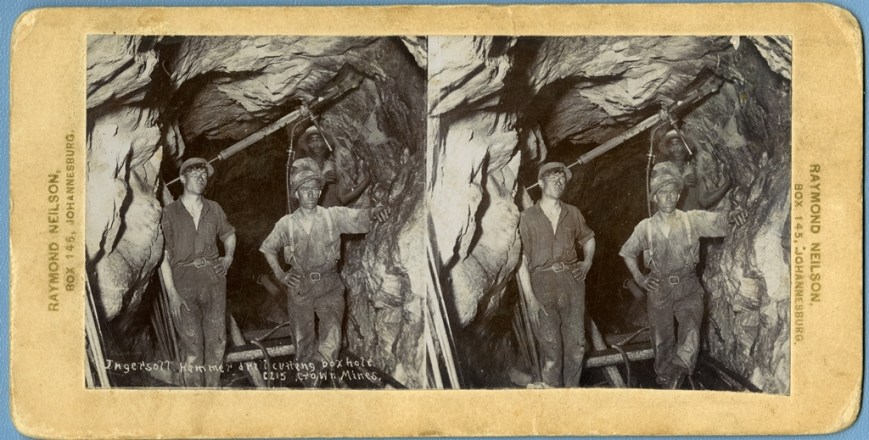
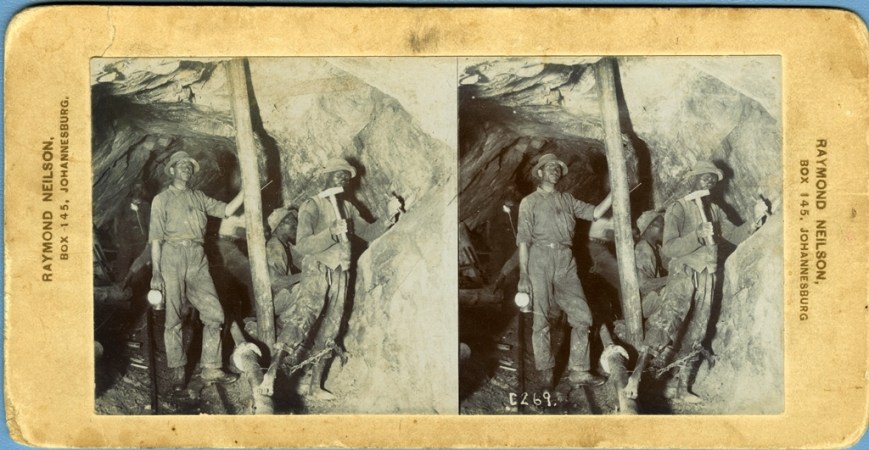
Each thick, oblong card with its rounded, scuffed edges discoloured by age has two seemingly identical images on it, side by side, and is embossed with the name of what I guess must have been the photographer or printing studio’s name in gold down the margin: “RAYMOND NEILSON, BOX 145, JOHANNESBURG”. The images depict miners underground. Some are very faded, to the extent that the figures in them appear featureless and ghostly. There is virtually no annotation on most of the photos. On just a few of them, spidery white handwriting on the photo itself, as if scratched into the negative before it was printed, announces the name of the machinery or activity in the picture and the name of the mine: “Crown Mines”.
I pick up the first card, slot it into the stereoscope, and peer through the device. On the left of the two images, the writing announces: “Ingersoll hammer drill cutting box hole. C215. Crown Mines.”
I slide the holder backwards and forwards along the wooden shaft to focus. I’m seeing two images, nothing remarkable, until suddenly, at a precise point on the axis, the images coalesce into one, three-dimensional. The experience is that of a gestalt switch, the optical illusion uncanny. I blink hard. It’s still there. It feels magical, as if the figures in the photos are stepping right out of the card towards me. Their eyes stare into mine through over a century of time, gleaming white out of dirty, sweaty faces.
Startlingly tangible, here stand two young white men in a mine shaft, scarcely out of their teens, leaning against rock, each with a hand on a hip and a jauntily cocked hat. They are very young… yet very old too, I immediately think: definitely dead now; and perhaps dead soon after the picture was taken, living at risk, killed in a rock fall or in World War One. A pang of indefinable emotion hits. I am amazed at how powerfully this image has flooded my imagination. Even with the difficult viewing process, the effect is astonishing.
I am reminded of Susan Sontag’s contention that all photographs are memento mori: “To take a photograph is to participate in another person’s (or thing’s) mortality, vulnerability, mutability. Precisely by slicing out this moment and freezing it, all photographs testify to time’s relentless melt”5.
I also notice that the trick of parallax (and concurrently, the evocativeness) works most pronouncedly on the figures in the foreground, probably due to the camera angle and vanishing points of the perspective. Behind the two white youngsters, almost fading into the darkness, is a black man, holding up a drill over all of their heads that seems to penetrate the tunnel of rock in which they are suspended.
He appears to have moved during the shot as his face is blurred. This could also be due to the low light in the shaft. Though he is looking straight at me, I can’t connect with him like I do with the figures in front. He is very much in the background, a presence without substance. The way the photo was set up and taken has placed him in that position, and this viewpoint is indelible, no matter how hard I try to look past it.
There is no writing on this one except for what seems to be a reference number: “C269”. The figure in the foreground is a black man, miming work with a mallet and chisel against the rock face, though clearly standing very still for the shot, as he is perfectly in focus, his sceptical gaze on us, a sharp shadow thrown on the rock behind him. This is no ordinary lamp light: it seems clear that these pictures have been professionally illumined by the photographer, perhaps using magnesium flares, because these shots definitely predate flash photography.
To the man with the chisel’s left stands a white man, face dark with dirt. He is holding a lamp in one hand, and his other grasps a support pile which bisects the shaft and also the photo. Tight-jawed, he stares beyond us, his eyes preoccupied, glazed over. Behind the two men in the foreground, there are more men – parts of two, perhaps three workers can be seen, one a black man crouched down at the rock face behind the man with the chisel.
What strikes me most trenchantly about this picture — the punctum, after Barthes7 — is the man with the chisel’s bare feet. He is at work in an extremely hazardous environment without shoes. Looking at all the photographs, every white worker is wearing boots, but there are several pictures where it is visible that many of the black workers are barefoot.
This is shocking visual evidence of an exploitative industry which does not take its workers’ safety seriously: these men are placed at incredible risk without the provision of adequate protective attire: none have hard protection for their heads, and black workers are without shoes. Men not deemed worthy of protection are, by inference, expendable. From these photos, one surmises that black lives are more dispensable than white.
I am really curious to find out more about these pictures. Perhaps the visual evidence here is echoed in literature? Perhaps they can tell us things the literature does not?
Who were these people posing? There is nothing on the back of the photos. No captions, no dates. Who was the photographer? For what purpose were these pictures being taken? The lack of answers to these most mundane of questions lends the photos an uncanny, almost spectral quality.
pharmakon interview (2015)
Great Interview with Margaret Chardiet AKA “Pharmakon” in Santiago, Chile, September 02, 2015, for her South American Tour “Sacred Bones”.
nostalghia (1983)
Russian director Andrei Tarkovsky’s film from 1983. I’m not going to link to any analysis here because to do so would narrow the interpretive possibilities of this opaque, allegorical masterpiece. Very superficially, though, the storyline is about a writer who, trapped by his fame and an unhappy marriage, seeks out his cultural past in Italy. Here he meets a local pariah who declares that the world is coming to an end. The writer finds this prophecy curiously more alluring than the possibility of a dead-end future. Nostalghia won the Grand Prix de Creation and the International Critics Prize at the 1984 Cannes Film Festival.
You can pick (slightly crappy) subtitles in several languages.
leigh-ann naidoo – hallucinations (17 august 2016)
“Quite simply – and this is what I wish to discuss tonight in relation to the question of rage and violence – we are living in different times. Or at least, our time is disjointed, out of sync, plagued by a generational fault line that scrambles historicity.
“The spectre of revolution, of radical change, is in young peoples’ minds and politics, and it is almost nowhere in the politics of the anti-apartheid generation. In fact, even as they criticised young people just five years earlier for being apathetic and depoliticized, they have now thought student activists misguided, uninformed, and mad.
“You would think that it might be possible to resolve this difference in time by means of a careful reading of what is called the ‘objective conditions for revolution’: are we in fact in a time in which revolution is immanent? No matter the subjective experience of time – there must be a way of determining who has the better bearing on history, who can tell the time. What time is it? Yet to tell the time is a complex matter in this society.
“We are, to some degree, post-apartheid, but in many ways not at all. We are living in a democracy that is at the same time violently, pathologically unequal. Protest action against the government – huge amounts of it, what in most other places would signal the beginning of radical change – often flips into a clamour for favour from that very government. Our vacillations, contradictions and anachronisms are indication that what time it is, is open to interpretation.
“I want to argue that the comrades I have worked with in the student movement are not so much mad as they are time-travellers. Or rather, that their particular, beautiful madness is to have recognised and exploited the ambivalence of our historical moment to push into the future. They have been working on the project of historical dissonance, of clarifying the untenable status quo of the present by forcing an awareness of a time when things are not this way. They have seen things many have yet to see. They have been experimenting with hallucinating a new time…”
__
Read the rest of this paper, delivered at the 13th annual Ruth First Memorial Lecture at Wits University in Johannesburg last night.
simone weil – the ring of gyges
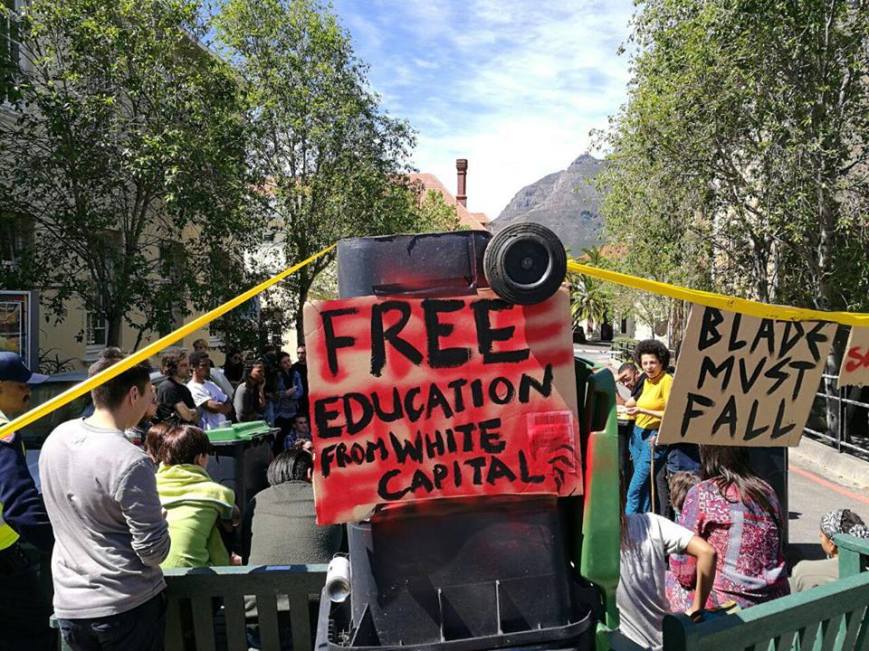
REMEMBER MARIKANA
 … We set things aside without knowing we are doing so; that is precisely where the danger lies. Or, which is still worse, we set them aside by an act of the will, but by an act of the will that is furtive in relation to ourselves. Afterwards we do not any longer know that we have set anything aside. We do not want to know it, and, by dint of not wanting to know it, we reach the point of not being able to know it.
… We set things aside without knowing we are doing so; that is precisely where the danger lies. Or, which is still worse, we set them aside by an act of the will, but by an act of the will that is furtive in relation to ourselves. Afterwards we do not any longer know that we have set anything aside. We do not want to know it, and, by dint of not wanting to know it, we reach the point of not being able to know it.
This faculty of setting things aside opens the door to every sort of crime. Outside those departments where education and training have forged solid links, it provides a key to absolute licence. That is what makes it possible for men to behave in such an incoherent fashion, particularly wherever the social, collective emotions play a part (war, national or class hatreds, patriotism for a party or a church). Whatever is surrounded with the prestige of the social element is set in a different place from other things and is exempt from certain connexions.
We also make use of this key when we give way to the allurements of pleasure.
I use it when, day after day, I put off the fulfillment of some obligation. I separate the obligation and the passage of time.
There is nothing more desirable than to get rid of this key. It should be thrown to the bottom of a well whence it can never again be recovered.
The ring of Gyges who has become invisible—this is precisely the act of setting aside: setting oneself aside from the crime one commits; not establishing the connexion between the two.
The act of throwing away the key, of throwing away the ring of Gyges—this is the effort proper to the will. It is the act by which, in pain and blindness, we make our way out of the cave. Gyges: ‘I have become king, and the other king has been assassinated.’ No connexion whatever between these two things. There we have the ring!

The owner of a factory: ‘I enjoy this and that expensive luxury and my workmen are miserably poor.’ He may be very sincerely sorry for his workmen and yet not form the connexion.
For no connexion is formed if thought does not bring it about. Two and two remain indefinitely as two and two unless thought adds them together to make them into four.
We hate the people who try to make us form the connexions we do not want to form.
Justice consists of establishing between analogous things connexions identical with those between similar terms, even when some of these things concern us personally and are an object of attachment for us.
This virtue is situated at the point of contact of the natural and the supernatural. It belongs to the realm of the will and of clear understanding, hence it is part of the cave (for our clarity is a twilight), but we cannot hold on to it unless we pass into the light.
__
Excerpted from Simone Weil‘s Gravity and Grace. First French edition 1947. Translated by Emma Crawford. English language edition 1963. Routledge and Kegan Paul, London.
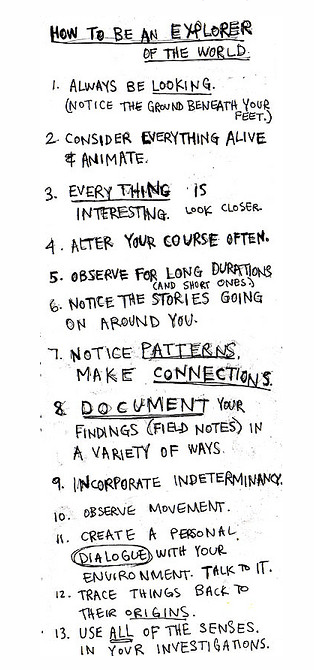
keri smith – how to be an explorer of the world
henry van dyke on doing things
“Use what talents you possess; the woods would be very silent if no birds sang there except those that sang best.”

jacky bowring – a field guide to melancholy (2008)
“Melancholy is a twilight state; suffering melts into it and becomes a sombre joy. Melancholy is the pleasure of being sad.”
– Victor Hugo, Toilers of the Sea
Melancholy is ambivalent and contradictory. Although it seems at once a very familiar term, it is extraordinarily elusive and enigmatic. It is something found not only in humans – whether pathological, psychological, or a mere passing mood – but in landscapes, seasons, and sounds. They too can be melancholy. Batman, Pierrot, and Hamlet are all melancholic characters, with traits like darkness, unrequited longing, and genius or heroism. Twilight, autumn and minor chords are also melancholy, evoking poignancy and the passing of time.
How is melancholy defined? A Field Guide to Melancholy traces out some of the historic traditions of melancholy, most of which remain today, revealing it to be an incredibly complex term. Samuel Johnson’s definition, in his eighteenth century Dictionary of the English Language, reveals melancholy’s multi-faceted nature was already well established by then: ‘A disease, supposed to proceed from a redundance of black bile; a kind of madness, in which the mind is always fixed on one object; a gloomy, pensive, discontented temper.’2 All of these aspects – disease, madness and temperament – continue to coalesce in the concept of melancholy, and rather than seeking a definitive definition or chronology, or a discipline-specific account, this book embraces contradiction and paradox: the very kernel of melancholy itself.
As an explicit promotion of the ideal of melancholy, the Field Guide extols the benefits of the pursuit of sadness, and questions the obsession with happiness in contemporary society. Rather than seeking an ‘architecture of happiness’, or resorting to Prozac-with-everything, it is proposed that melancholy is not a negative emotion, which for much of history it wasn’t – it was a desirable condition, sought for its ‘sweetness’ and intensity. It remains an important point of balance – a counter to the ‘loss of sadness’. Not grief, not mourning, not sorrow, yet all of those things.
Melancholy is profoundly interdisciplinary, and ranges across fields as diverse as medicine, literature, art, design, psychology and philosophy. It is over two millennia old as a concept, and its development predates the emergence of disciplines.While similarly enduring concepts have also been tackled by a breadth of disciplines such as philosophy, art and literature, melancholy alone extends across the spectrum of arts and sciences, with significant discourses in fields like psychiatry, as much as in art. Concepts with such an extensive period of development (the idea of ‘beauty’ for example) tend to go through a process of metamorphosis and end up meaning something distinctly different.3 Melancholy has been surprisingly stable. Despite the depth and breadth of investigation, the questions, ideas and contradictions which form the ‘constellation’4 of melancholy today are not dramatically different from those at any time in its history. There is a sense that, as psychoanalytical theorist Julia Kristeva puts it, melancholy is ‘essential and trans-historical’.5
Melancholy is a central characteristic of the human condition, and Hildegard of Bingen, the twelfth century abbess and mystic, believed it to have been formed at the moment that Adam sinned in taking the apple – when melancholy ‘curdled in his blood’.6 Modern day Slovenian philosopher, Slavoj Žižek, also positions melancholy, and its concern with loss and longing, at the very heart of the human condition, stating ‘melancholy (disappointment with all positive, empirical objects, none of which can satisfy our desire) is in fact the beginning of philosophy.’7
The complexity of the idea of melancholy means that it has oscillated between attempts to define it scientifically, and its embodiment within a more poetic ideal. As a very coarse generalisation, the scientific/psychological underpinnings of melancholy dominated the early period, from the late centuries BC when ideas on medicine were being formulated, while in later, mainly post-medieval times, the literary ideal became more significant. In recent decades, the rise of psychiatry has re-emphasised the scientific dimensions of melancholy. It was never a case of either/or, however, and both ideals, along with a multitude of other colourings, have persisted through history.
The essential nature of melancholy as a bodily as well as a purely mental state is grounded in the foundation of ideas on physiology; that it somehow relates to the body itself. These ideas are rooted in the ancient notion of ‘humours’. In Greek and Roman times humoralism was the foundation for an understanding of physiology, with the four humours ruling the body’s characteristics.
Phlegm, blood, yellow bile and black bile were believed to be the four governing elements, and each was ascribed to particular seasons, elements and temperaments. This can be expressed via a tetrad, or four-cornered diagram.
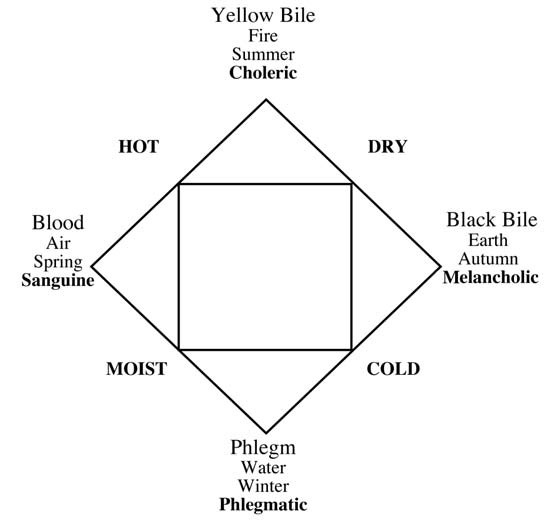
The Four Humours, adapted from Henry E Sigerist (1961) “A History of Medicine”, 2 vols New York: Oxford University Press, 2:232
The four-part divisions of temperament were echoed in a number of ways, as in the work of Alkindus, the ninth century Arab philosopher, who aligned the times of the day with particular dispositions. The tetrad could therefore be further embellished, with the first quarter of the day sanguine, second choleric, third melancholic and finally phlegmatic. Astrological allegiances reinforce the idea of four quadrants, so that Jupiter is sanguine, Mars choleric, Saturn is melancholy, and the moon or Venus is phlegmatic. The organs, too, are associated with the points of the humoric tetrad, with the liver sanguine, the gall bladder choleric, the spleen melancholic, and the brain/ lungs phlegmatic.
Melancholy, then, is associated with twilight, autumn, earth, the spleen, coldness and dryness, and the planet Saturn. All of these elements weave in and out of the history of melancholy, appearing in mythology, astrology, medicine, literature and art.The complementary humours and temperaments were sometimes hypothesised as balances, so that the opposite of one might be introduced as a remedy for an excess of another. For melancholy, the introduction of sanguine elements – blood, air and warmth – could counter the darkness. This could also work at an astrological level, as in the appearance of the magic square of Jupiter on the wall behind Albrecht Dürer’s iconic engraving Melencolia I, (1514) – the sign of Jupiter to introduce a sanguine balance to the saturnine melancholy angel.
In this early phase of the development of humoral thinking a key tension arose, as on one hand it was devised as a means of establishing degrees of wellness, but on the other it was a system of types of disposition. As Klibansky, Panofsky and Saxl put it, there were two quite different meanings to the terms sanguine, choleric, phlegmatic and melancholy, as either ‘pathological states or constitutional aptitudes’.9 Melancholy became far more connected with the idea of illness than the other temperaments, and was considered a ‘special problem’.
The blurry boundary between an illness and a mere temperament was a result of the fact that many of the symptoms of ‘melancholia’ were mental, and thus difficult to objectify, unlike something as apparent as a disfigurement or wound. The theory of the humours morphed into psychology and physiognomy, with particular traits or appearances associated with each temperament.
Melancholy was aligned with ‘the lisping, the bald, the stuttering and the hirsute’, and ‘emotional disturbances’ were considered as indicators of ‘mental melancholy’.10 Hippocrates in his Aphorismata, or ‘Aphorisms’, in 400 BC noted, ‘Constant anxiety and depression are signs of melancholy.’ Two centuries later the physician Galen, in an uncharacteristically succinct summation, noted that Hippocrates was ‘right in summing up all melancholy symptoms in the two following: Fear and Depression.’11
The foundations of the ideas on melancholy are fraught with complexity and contradiction, and this signals the beginning of a legacy of richness and debate. We have a love-hate relationship with melancholy, recognising its potential, yet fearing its connotations. What is needed is some kind of guide book, to know how to recognise it, where to find it – akin to the Observer’s Guides, the Blue Guides, or Gavin Pretor-Pinney’s The Cloudspotter’s Guide. Yet, to attempt to write a guide to such an amorphous concept as melancholy is overwhelmingly impossible, such is the breadth and depth of the topic, the disciplinary territories, the disputes, and the extensive creative outpourings. There is a tremendous sense of the infinite, like staring at stars, or at a room full of files, a daunting multitude. The approach is, therefore, to adopt the notion of the ‘constellation’, and to plot various points and co-ordinates, a join-the-dots approach to exploration which roams far and wide, and connects ideas and examples in a way which seeks new combinations and sometimes unexpected juxtapositions.
A Field Guide to Melancholy is therefore in itself a melancholic enterprise: for the writer, and the reader, the very idea of a ‘field guide’ to something so contradictory, so elusive, embodies the impossibility and futility that is central to melancholy’s yearning. Yet, it is this intangible, potent possibility which creates melancholy’s magnetism, recalling Joseph Campbell’s version of the Buddhist advice to “joyfully participate in the sorrows of the world”.12
Notes
1. Victor Hugo, Toilers of the Sea, vol. 3, p.159.
2. Samuel Johnson, A Dictionary of the English Language, p.458, emphasis mine.
3. This constant shift in the development of concepts is well-illustrated by Umberto Eco (ed) (2004) History of Beauty, New York: Rizzoli, and his recent (2007) On Ugliness, New York: Rizzoli.
4. The term ‘constellation’ is Giorgio Agamben’s, and captures the sense of melancholy’s persistence as a collection of ideas, rather than one simple definition. See Giorgio Agamben, Stanzas:Word and Phantasm in Western Culture, p.19.
5. Julia Kristeva, Black Sun: Depression and Melancholia, p.258.
6. Raymond Klibansky, Erwin Panofsky and Fritz Saxl, Saturn and Melancholy: Studies in the History of Natural Philosophy, Religion and Art, p.79.
7. Slavoj Žižek, Did Somebody say Totalitarianism? Five Interventions on the (Mis)use of a Notion, p.148.
8. In Stanley W Jackson (1986), Melancholia and Depression: From Hippocratic Times to Modern Times, p.9.
9. Raymond Klibansky, Erwin Panofsky and Fritz Saxl, Saturn and Melancholy: Studies in the History of Natural Philosophy, Religion and Art, p.12.
10. ibid, p.15.
11. ibid, p.15, and n.42.
12. A phrase used by Campbell in his lectures, for example on the DVD Joseph Campbell (1998) Sukhavati. Acacia.
__
Excerpted from the introduction to Jacky Bowring’s A Field Guide to Melancholy, Oldcastle Books, 2008.
jacques derrida & “the science of ghosts” (1983)
Jacques Derrida appearing as himself in Ken McMullen’s Ghost Dance, interviewed by Pascale Ogier in 1983. He’s talking about #PokémonGo from 3:40 ;).
the awakening woman
The Awakening Woman is consciously aware of herself and strives to be intimate with all facets of her being. She is her own person as well as relational. She nurtures and honors the relationship with herself as well as with others. She is actively awakening and supports the awakening of those around her. Her devotion to herself allows her devotion to others to be genuine and nourishing. She is sincere, authentic, vulnerable and strong. She is protective, and accepts and values protection from others when appropriate. She establishes healthy boundaries while keeping an open heart.
The Awakening Woman is intimate with her painbody and the feminine wound. She does not deny her pain, but turns towards it for healing. She knows that the dysfunctional views and oppression of females/femaleness is nothing she caused, but acknowledges the ways in which she has participated or was complacent in the unjust treatment of…
View original post 1,125 more words
gayatri spivak at uct next week
The Institute for Creative Arts is proud to present internationally renowned theorist, Professor Gayatri Spivak.
Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak is one of the most significant and influential literary theorists of our time.
Having first come to prominence with her translation of Derrida’s Of Grammatology in 1976, Spivak has since applied deconstructive readings to theoretical engagements and textual analyses including feminism, Marxism, literary criticism and postcolonialism – capturing complex theories that transgress disciplinary boundaries.
The Institute for Creative Arts (ICA, formerly GIPCA) in collaboration with UCT’s Black Academic Caucus (BAC) is honoured to present this esteemed academic and philosopher as part of the ICA’s Great Texts/Big Questions lecture series.
Of her address, entitled “Still hoping for a revolution”, Spivak writes:
Now that the first wave of “revolution” against decrepit empires, leading to state capitalism and vanguardism, is showing its deep fault lines, I reopen the question of Marx’s real project and focus on holistic education into citizenship – as the conjuncture has moved from the central agency of the industrial proletariat – as a robust substitute for both vanguardism and techniques of pre-party formation.
This is particularly interesting for me because I have myself learned from many mistakes made since 1992, when I presented the T.B. Davie Memorial Lecture in Cape Town on “Thinking Academic Freedom in Gendered Post-Coloniality.” The general response, as I heard it reported, was “we already do this.” Yet, in 2002, Joan Vincent included the piece in her The Anthropology of Politics: A Reader in Ethnography, Theory, and Critique, commenting that I had been “prescient.” I therefore hope that my audience, which will be different, will also have learned from past “mistakes.”
Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak is currently professor of Comparative Literature at Columbia University where she founded the Institute for Comparative Literature and Society. Her critical writings include Of Grammatology (1976), In Other Worlds: Essays in Cultural Politics (1987), The Post-Colonial Critic (1990), Thinking Academic Freedom in Gendered Post-Coloniality (1992), Outside in the Teaching Machine (1993), A Critique of Postcolonial Reason (1999), Death of a Discipline (2003), and Other Asias (2005).
The lecture, followed by an open question and answer session, will take place from 17:30 – 19:00 on Friday 22 July 2016 at Jameson Hall, University Avenue, University of Cape Town Upper Campus.
Refreshments will be served from 17:00.
No booking is necessary and all are welcome.
For more information, contact the ICA office: +27 21 650 7156 or ica@uct.ac.za
alden wood – radical intersections: the rise of atonal music and the invisible committee’s “the coming insurrection”
 The Coming Insurrection, a notorious 2007 ultra-left polemical tract written by a collective of French anti-state communists writing under the group-moniker The Invisible Committee, posits a conception of insurrection as the creation of new collective ontologies through acts of radical social rupture. Eschewing the orthodox Marxist line that revolution is something temporally removed from the present, towards which pro-revolutionaries must organize and work, The Invisible Committee’s use of insurrection claims it as an antagonistic challenge to late-capitalism firmly grounded in its own immediacy. Communism is therefore made immediate, and it is willed into being by insurrectionary acts of social rupture.
The Coming Insurrection, a notorious 2007 ultra-left polemical tract written by a collective of French anti-state communists writing under the group-moniker The Invisible Committee, posits a conception of insurrection as the creation of new collective ontologies through acts of radical social rupture. Eschewing the orthodox Marxist line that revolution is something temporally removed from the present, towards which pro-revolutionaries must organize and work, The Invisible Committee’s use of insurrection claims it as an antagonistic challenge to late-capitalism firmly grounded in its own immediacy. Communism is therefore made immediate, and it is willed into being by insurrectionary acts of social rupture.
While much has been written on the debt that The Invisible Committee owes to French strains of ultra-left anti-state communism, Michel Foucault, Gilles Deleuze, Giorgio Agamben, Situationism, and the Italian Autonomia movement of the 1970s, their implicit nod to the sociopolitical themes of music has been largely ignored. By subtly claiming that insurrection spreads by resonance and that such proliferation “takes the shape of a music,” The Invisible Committee allows for the interpretation of its “coming insurrection” as an inherently musical act. Using a historical reading of the shift from tonality to atonality in Western art music, as exemplified by Arnold Schoenberg, Alden Wood’s interpretation of The Coming Insurrection aims at imbuing its explicitly political premises with a more thorough exploration of its implicit musical qualities.
Published in Interdisciplinary Humanities Vol. 30 pp. 57-65, 2013.
theodore isaac rubin on kindness
Still true.

carl jung on the projection of evil (1957)
Quite apart from the barbarities and blood baths perpetrated by the Christian nations among themselves throughout European history, the European has also to answer for all the crimes he has committed against the dark-skinned peoples during the process of colonization.
In this respect the white man carries a very heavy burden indeed.
It shows us a picture of the common human shadow that could hardly be painted in blacker colors.
The evil that comes to light in man and that undoubtedly dwells within him is of gigantic proportions, so that for the Church to talk of original sin and to trace it back to Adam’s relatively innocent slip-up with Eve is almost a euphemism.
The case is far graver and is grossly underestimated.
Since it is universally believed that man is merely what his consciousness knows of itself, he regards himself as harmless and so adds stupidity to iniquity. He does not deny that terrible things have happened and still go on happening, but it is always “the others” who do them.
And when such deeds belong to the recent or remote past, they quickly and conveniently sink into the sea of forgetfulness, and that state of chronic woolly-mindedness returns which we describe as “normality.”
In shocking contrast to this is the fact that nothing has finally disappeared and nothing has been made good.
The evil, the guilt, the profound unease of conscience, the obscure misgiving are there before our eyes, if only we would see. Man has done these things; I am a man, who has his share of human nature; therefore I am guilty with the rest and bear unaltered and indelibly within me the capacity and the inclination to do them again at any time.
Even if, juristically speaking, we were not accessories to the crime, we are always, thanks to our human nature, potential criminals.
In reality we merely lacked a suitable opportunity to be drawn into the infernal melée. None of us stands outside humanity’s black collective shadow.
Whether the crime lies many generations back or happens today, it remains the symptom of a disposition that is always and everywhere present – and one would therefore do well to possess some “imagination in evil”, for only the fool can permanently neglect the conditions of his own nature.
In fact, this negligence is the best means of making him an instrument of evil.
Harmlessness and naïveté are as little helpful as it would be for a cholera patient and those in his vicinity to remain unconscious of the contagiousness of the disease.
On the contrary, they lead to projection of the unrecognized evil into the “other.”
This strengthens the opponent’s position in the most effective way, because the projection carries the fear which we involuntarily and secretly feel for our own evil over to the other side and considerably increases the formidableness of his threat.
What is even worse, our lack of insight deprives us of the capacity to deal with evil.
Here, of course, we come up against one of the main prejudices of the Christian tradition, and one that is a great stumbling block to our policies.
We should, so we are told, eschew evil and, if possible, neither touch nor mention it. For evil is also the thing of ill omen, that which is tabooed and feared.
This attitude towards evil, and the apparent circumventing of it, flatter the primitive tendency in us to shut our eyes to evil and drive it over some frontier or other, like the Old Testament scapegoat, which was supposed to carry the evil into the wilderness.
But if one can no longer avoid the realization that evil, without man’s ever having chosen it, is lodged in human nature itself, then it bestrides the psychological stage as the equal and opposite partner of good.
This realization leads straight to a psychological dualism, already unconsciously prefigured in the political world schism and in the even more unconscious dissociation in modern man himself. The dualism does not come from this realization; rather, we are in a split condition to begin with.
It would be an insufferable thought that we had to take personal responsibility for so much guiltiness. We therefore prefer to localize the evil with individual criminals or groups of criminals, while washing our hands in innocence and ignoring the general proclivity to evil.
This sanctimoniousness cannot be kept up, in the long run, because the evil, as experience shows, lies in man – unless, in accordance with the Christian view, one is willing to postulate a metaphysical principle of evil.
The great advantage of this view is that it exonerates man’s conscience of too heavy a responsibility and fobs it off on the devil, in correct psychological appreciation of the fact that man is much more the victim of his psychic constitution than its inventor.
Considering that the evil of our day puts everything that has ever agonized mankind in the deepest shade, one must ask oneself how it is that, for all our progress in the administration of justice, in medicine and in technology, for all our concern for life and health, monstrous engines of destruction have been invented which could easily exterminate the human race.
No one will maintain that the atomic physicists are a pack of criminals because it is to their efforts that we owe that peculiar flower of human ingenuity, the hydrogen bomb.
The vast amount of intellectual work that went into the development of nuclear physics was put forth by men who devoted themselves to their task with the greatest exertions and self-sacrifice and whose moral achievement could just as easily have earned them the merit of inventing something useful and beneficial to humanity.
But even though the first step along the road to a momentous invention may be the outcome of a conscious decision, here, as everywhere, the spontaneous idea – the hunch or intuition – plays an important part.
In other words, the unconscious collaborates too and often makes decisive contributions.
So it is not the conscious effort alone that is responsible for the result; somewhere or other the unconscious, with its barely discernible goals and intentions, has its finger in the pie.
If it puts a weapon in your hand, it is aiming at some kind of violence.
Knowledge of the truth is the foremost goal of science, and if in pursuit of the longing for light we stumble upon an immense danger, then one has the impression more of fatality than of premeditation.
It is not that present-day man is capable of greater evil than the man of antiquity or the primitive. He merely has incomparably more effective means with which to realize his proclivity to evil.
As his consciousness has broadened and differentiated, so his moral nature has lagged behind. That is the great problem before us today. Reason alone does not suffice.
— From The Undiscovered Self (1957).
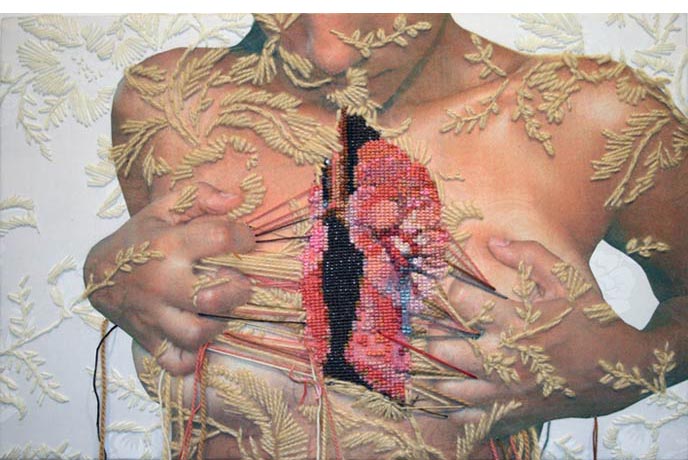
katie collins – woven into the fabric of the text (2016)
The following is excerpted from a feature essay on the LSE blog by Katie Collins, entitled “Woven into the Fabric of the Text: Subversive Material Metaphors in Academic Writing”. Collins proposes that we shift our thinking about academic writing from building metaphors – the language of frameworks, foundations and buttresses – to stitching, sewing and piecing. Needlecraft metaphors offer another way of thinking about the creative and generative practice of academic writing as decentred, able to accommodate multiple sources and with greater space for the feminine voice.
__
[W]hy do I regard switching from a metaphor of building to one of stitching as a subversive act? For several reasons. Throughout history, needlework has been a marker of femininity in its various iterations, a means to inculcate it, and something to sneer at as a way of shoring up women’s supposed inferiority. Theodore Roethke described women’s poetry as ‘the embroidering of trivial themes […] running between the boudoir and the alter, stamping a tiny foot against God…’ (165), for example. Women’s naturally nimble fingers were to be occupied; we were to be kept out of the way and out of trouble, shut in the top room of a circular tower and thus prevented from engaging in the masculine pursuits of politics, thinking, reading and writing and making Art (for a fascinating discussion on women, folk art and cultural femicide, I recommend this post by Dr Lucy Allen). The frills and fripperies our needles produced were ample evidence, should anyone require it, that we were frivolous creatures entirely unsuited to public life. Or so the story was. So using needlework metaphors in my academic writing blows a resonant raspberry to that notion, for one thing. But the subversion here is not as straightforward as reclamation, of presenting something usually disparaged as having value after all. Femininity and its inculcation is a displeasingly twisted yarn of benevolence and belittlement. The trick is to unpick the knots without snapping the thread and unravelling the beautiful work, to value that which has been constructed as feminine while at the same time escaping its constricting net.
Imagining academic writing as piecing fragments is one way of recognising that it can integrate all sorts of sources but, more significantly, piecing is also a decentred activity. When quilting, one can plan, cut and stitch many individual squares whenever there is a moment spare, before bringing them together to form the overall pattern, which is flat and in aesthetic terms may have no centre or many centres, and no predetermined start or end. This holds true both for the practice of quilting and how we might think differently about academic writing, with each contribution not a brick in a structured wall but a square ready to stitch onto other squares to make something expected or unexpected, the goal depth and intensity rather than progress (see Mara Witzling). There is sedition here in several senses. This way of imagining how writing works is not individualistic or competitive. Each voice is a thread, and only when they are woven together do they form a whole, as Ann Hamilton’s tapestries represent social collaboration and interconnectedness; many voices not one, cut from the same cloth or different.
But acknowledging that one might have to fit the work of writing around other things, a problem that has occupied me from the moment I became a mother, is a particularly rebellious act, I think. As Adrienne Rich expresses in the poem ‘Transcendental Etude’:
Vision begins to happen in such a life
as if a woman quietly walked away
from the argument and jargon in a room
and sitting down in the kitchen, began turning in her lap
bits of yarn, calico and velvet scraps,
laying them out absently on the scrubbed boards
in the lamplight, with small rainbow-colored shells
sent in cotton-wool from somewhere far away,
and skeins of milkweed from the nearest meadow –
original domestic silk, the finest findings.
This way of imagining academic writing as something that is part of life, rather than something apart, challenges the view of the scholar as the extraordinary, solitary genius who sits alone in his study day after day while the minutiae of clothing and food is organised for him, around him, despite him. But with metaphors that emphasise the piecing of fragments, both everyday and exceptional, we recognise a way of working in which every fragment that can be pieced together into a square is ‘the preservation of a woman’s voice’.
Read the whole of this great essay by Katie Collins HERE.
simone weil – algebra
 Money, mechanization, algebra. The three monsters of contemporary civilization. Complete analogy.
Money, mechanization, algebra. The three monsters of contemporary civilization. Complete analogy.
Algebra and money are essentially levellers, the first intellectually, the second effectively.
About fifty years ago the life of the Provençal peasants ceased to be like that of the Greek peasants described by Hesiod. The destruction of science as conceived by the Greeks took place at about the same period. Money and algebra triumphed simultaneously.
The relation of the sign to the thing signified is being destroyed, the game of exchanges between signs is being multiplied of itself and for itself. And the increasing complication demands that there should be signs for signs… [Note that this comment comes decades before Baudrillard writes about simulacra in 1981.]
Among the characteristics of the modern world we must not forget the impossibility of thinking in concrete terms of the relationship between effort and the result of effort. There are too many intermediaries. As in the other cases, this relationship which does not lie in any thought, lies in a thing: money.
As collective thought cannot exist as thought, it passes into things (signs, machines…). Hence the paradox: it is the thing which thinks and the man who is reduced to the state of a thing.
There is no collective thought. On the other hand our science is collective like our technics. Specialization. We inherit not only results but methods which we do not understand. For the matter of that the two are inseparable, for the results of algebra provide methods for the other sciences.
To make an inventory or criticism of our civilization—what does that mean? To try to expose in precise terms the trap which has made man the slave of his own inventions. How has unconsciousness infiltrated itself into methodical thought and action?
To escape by a return to the primitive state is a lazy solution. We have to rediscover the original pact between the spirit and the world in this very civilization of which we form a part. But it is a task which is beyond our power on account of the shortness of life and the impossibility of collaboration and of succession. That is no reason for not undertaking it. The situation of all of us is comparable to that of Socrates when he was awaiting death in his prison and began to learn to play the lyre… At any rate we shall have lived…
The spirit, overcome by the weight of quantity, has no longer any other criterion than efficiency.
Modern life is given over to immoderation. Immoderation invades everything: actions and thought, public and private life.
The decadence of art is due to it. There is no more balance anywhere. The Catholic movement is to some extent in reaction against this; the Catholic ceremonies, at least, have remained intact. But then they are unrelated to the rest of existence.
Capitalism has brought about the emancipation of collective humanity with respect to nature. But this collective humanity has itself taken on with respect to the individual the oppressive function formerly exercised by nature.
This is true even with material things: fire, water etc. The community has taken possession of all these natural forces.
Question: can this emancipation, won by society, be transferred to the individual?
__
Excerpted from Simone Weil‘s Gravity and Grace. First French edition 1947. Translated by Emma Crawford. English language edition 1963. Routledge and Kegan Paul, London.
simone weil – beauty
 Beauty is the harmony of chance and the good.
Beauty is the harmony of chance and the good.
Beauty is necessity which, while remaining in conformity with its own law and with that alone, is obedient to the good.
The subject of science is the beautiful (that is to say order, proportion, harmony) in so far as it is suprasensible and necessary.
The subject of art is sensible and contingent beauty discerned through the network of chance and evil.
The beautiful in nature is a union of the sensible impression and of the sense of necessity. Things must be like that (in the first place), and, precisely, they are like that.
Beauty captivates the flesh in order to obtain permission to pass right to the soul.
Among other unions of contraries found in beauty there is that of the instantaneous and the eternal.
The beautiful is that which we can contemplate. A statue, a picture which we can gaze at for hours.
The beautiful is something on which we can fix our attention. Gregorian music. When the same things are sung for hours each day and every day, whatever falls even slightly short of supreme excellence becomes unendurable and is eliminated.
The Greeks looked at their temples. We can endure the statues in the Luxembourg because we do not look at them. A picture such as one could place in the cell of a criminal sentenced to solitary confinement for life without it being an atrocity, on the contrary.
Only drama without movement is truly beautiful. Shakespeare’s tragedies are second-class with the exception of Lear. Those of Racine, third-class except for Phèdre. Those of Corneille of the nth class.
A work of art has an author and yet, when it is perfect, it has something which is essentially anonymous about it. It imitates the anonymity of divine art. In the same way the beauty of the world proves there to be a God who is personal and impersonal at the same time and is neither the one nor the other separately.
The beautiful is a carnal attraction which keeps us at a distance and implies a renunciation. This includes the renunciation of that which is most deep-seated, the imagination. We want to eat all the other objects of desire. The beautiful is that which we desire without wishing to eat it. We desire that it should be.
We have to remain quite still and unite ourselves with that which we desire yet do not approach. We unite ourselves to God in this way: we cannot approach him.
Distance is the soul of the beautiful.
The attitude of looking and waiting is the attitude which corresponds with the beautiful. As long as one can go on conceiving, wishing, longing, the beautiful does not appear. That is why in all beauty we find contradiction, bitterness and absence which are irreducible.
Poetry: impossible pain and joy. A poignant touch, nostalgia. Such is Provençal and English poetry. A joy which by reason of its unmixed purity hurts, a pain which by reason of its unmixed purity brings peace.
Beauty: a fruit which we look at without trying to seize it.
The same with an affliction which we contemplate without drawing back.
A double movement of descent: to do again, out of love, what gravity does. Is not the double movement of descent the key to all art?*
This movement of descent, the mirror of grace, is the essence of all music. All the rest only serves to enshrine it.
The rising of the notes is a purely sensorial rising. The descent is at the same time a sensorial descent and a spiritual rising. Here we have the paradise which every being longs for: where the slope of nature makes us rise towards the good.
In everything which gives us the pure authentic feeling of beauty there really is the presence of God. There is as it were an incarnation of God in the world and it is indicated by beauty.
The beautiful is the experimental proof that the incarnation is possible.
Hence all art of the highest order is religious in essence. (That is what people have forgotten today.) A Gregorian melody is as powerful a witness as the death of a martyr.
If the beautiful is the real presence of God in matter and if contact with the beautiful is a sacrament in the full sense of the word, how is it that there are so many perverted aesthetes? Nero. Is it like the hunger of those who frequent black masses for the consecrated hosts? Or is it, more probably, because these people do not devote themselves to what is genuinely beautiful, but to a bad imitation? For, just as there, is an art which is divine, so there is one which is demoniacal. It was no doubt the latter that Nero loved. A great deal of our art is of the devil.
A person who is passionately fond of music may quite well be a perverted person—but I should find it hard to believe this of any one who thirsted for Gregorian chanting. [hahaha!]
We must certainly have committed crimes which have made us accursed, since we have lost all the poetry of the universe.
Art has no immediate future because all art is collective and there is no more collective life (there are only dead collections of people), and also because of this breaking of the true pact between the body and the soul. Greek art coincided with the beginning of geometry and with athleticism, the art of the Middle Ages with the craftsmen’s guilds, the art of the Renaissance with the beginning of mechanics, etc. … Since 1914 there has been a complete cut. Even comedy is almost impossible. There is only room for satire (when was it easier to understand Juvenal?).
Art will never be reborn except from amidst a general anarchy— it will be epic no doubt, because affliction will have simplified a great many things… Is it therefore quite useless for you to envy Leonardo or Bach. Greatness in our times must take a different course. Moreover it can only be solitary, obscure and without an echo… (but without an echo, no art).
__
* Descendit ad inferos… So, in another order, great art redeems gravity by espousing it out of love. [Editor’s note.]
__
Excerpted from Simone Weil‘s Gravity and Grace. First French edition 1947. Translated by Emma Crawford. English language edition 1963. Routledge and Kegan Paul, London.
robert greene – the 48 laws of power, or, how to be a consummately oppressive douchebag

Illustration by William Steig from Wilhelm Reich’s “Listen, Little Man” (1945)
LAW 1
NEVER OUTSHINE THE MASTER
Always make those above you feel comfortably superior. In your desire to please or impress them, do not go too far in displaying your talents or you might accomplish the opposite-inspire fear and insecurity. Make your masters appear more brilliant than they are and you will attain the heights of power.
LAW 2
NEVER PUT TOO MUCH TRUST IN FRIENDS, LEARN HOW TO USE ENEMIES
Be wary of friends-they will betray you more quickly, for they are easily aroused to envy. They also become spoiled and tyrannical. But hire a former enemy and he will be more loyal than a friend, because he has more to prove. In fact, you have more to fear from friends than from enemies. If you have no enemies, find a way to make them.
LAW 3
CONCEAL YOUR INTENTIONS
Keep people off-balance and in the dark, by never revealing the purpose behind your actions. If they have no clue what you are up to, they cannot prepare a defense. Guide them far enough down the wrong path, envelop them in enough smoke, and by the time they realize your intentions, it will be too late.
LAW 4
ALWAYS SAY LESS THAN NECESSARY
When you are trying to impress people with words, the more you say, the more common you appear, and the less in control. Even if you are saying something banal, it will seem original if you make it vague, open-ended, and sphinxlike. Powerful people impress and intimidate by saying less. The more you say, the more likely you are to say something foolish.
LAW 5
SO MUCH DEPENDS ON REPUTATION- GUARD IT WITH YOUR LIFE
Reputation is the cornerstone of power. Through reputation alone you can intimidate and win; once it slips, however, you are vulnerable, and will be attacked on all sides. Make your reputation unassailable. Always be alert to potential attacks and thwart them before they happen. Meanwhile, learn to destroy your enemies by opening holes in their own reputations. Then stand aside and let public opinion hang them.
LAW 6
COURT ATTENTION AT ALL COST
Everything is judged by its appearance; what is unseen counts for nothing. Never let yourself get lost in the crowd, then, or buried in oblivion. Stand out. Be conspicuous, at all cost. Make yourself a magnet of attention by appearing larger, more colorful, more mysterious than the bland and timid masses.
LAW 7
GET OTHERS TO DO THE WORK FOR YOU, BUT ALWAYS TAKE THE CREDIT
Use the wisdom, knowledge, and legwork of other people to further your own cause. Not only will such assistance save you valuable time and energy, it will give you a godlike aura of efficiency and speed. In the end your helpers will be forgotten and you will be remembered. Never do yourself what others can do for you.
LAW 8
MAKE OTHER PEOPLE COME TO YOU-USE BAIT IF NECESSARY
When you force the other person to act, you are the one in control. It is always better to make your opponent come to you, abandoning his own plans in the process. Lure him with fabulous gains-then attack. You hold the cards.
LAW 9
WIN THROUGH YOUR ACTIONS, NEVER THROUGH ARGUMENT
Any momentary triumph you think you have gained through argument is really a Pyrrhic victory: The resentment and ill will you stir up is stronger and lasts longer than any momentary change of opinion. It is much more powerful to get others to agree with you through your actions, without saying a word. Demonstrate, do not explicate.
LAW 10
INFECTION: AVOID THE UNHAPPY AND UNLUCKY
You can die from someone else’s misery-emotional states are as infectious as diseases. You may feel you are helping the drowning man but you are only precipitating your own disaster. The unfortunate sometimes draw misfortune on themselves; they will also draw it on you. Associate with the happy and fortunate instead.
LAW 11
LEARN TO KEEP PEOPLE DEPENDENT ON YOU
To maintain your independence you must always be needed and wanted. The more you are relied on, the more freedom you have. Make people depend on you for their happiness and prosperity and you have nothing to fear. Never teach them enough so that they can do without you.
LAW 12
USE SELECTIVE HONESTY AND GENEROSITY TO DISARM YOUR VICTIM
One sincere and honest move will cover over dozens of dishonest ones. Open-hearted gestures of honesty and generosity bring down the guard of even the most suspicious people. Once your selective honesty opens a hole in their armor, you can deceive and manipulate them at will. A timely gift-a Trojan horse-will serve the same purpose.
LAW 13
WHEN ASKING FOR HELP, APPEAL TO PEOPLE’S SELF-INTEREST, NEVER TO THEIR MERCY OR GRATITUDE
If you need to tum to an ally for help, do not bother to remind him of your past assistance and good deeds. He will find a way to ignore you. Instead, uncover something in your request, or in your alliance with him, that will benefit him, and emphasize it out of all proportion. He will respond enthusiastically when he sees some thing to be gained for himself.

From Wilhelm Reich’s “Listen, Little Man” (1945)
LAW 14
POSE AS A FRIEND, WORK AS A SPY
Knowing about your rival is critical. Use spies to gather valuable information that will keep you a step ahead. Better still: Play the spy yourself. In polite social encounters, learn to probe. Ask indirect questions to get people to reveal their weaknesses and intentions. There is no occasion that is not an opportunity for artful spying.
LAW 15
CRUSH YOUR ENEMY TOTALLY
All great leaders since Moses have known that a feared enemy must be crushed completely. (Sometimes they have learned this the hard way.) If one ember is left alight, no matter how dimly it smolders, afire will eventually break out. More is lost through stopping halfway than through total annihilation: The enemy will recover, and will seek revenge. Crush him, not only in body but in spirit.
LAW 16
USE ABSENCE TO INCREASE RESPECT AND HONOR
Too much circulation makes the price go down: The more you are seen and heard from, the more common you appear. If you are already established in a group, temporary withdrawal from it will make you more talked about, even more admired. You must learn when to leave. Create value through scarcity.
LAW 17
KEEP OTHERS IN SUSPENDED TERROR: CULTIVATE AN AIR OF UNPREDICTABILITY
Humans are creatures of habit with an insatiable need to see familiarity in other people’s actions. Your predictability gives them a sense of control. Tum the tables: Be deliberately unpredictable. Behavior that seems to have no consistency or purpose will keep them off-balance, and they will wear themselves out trying to explain your moves. Taken to an extreme, this strategy can intimidate and terrorize.
LAW 18
DO NOT BUILD FORTRESSES TO PROTECT YOURSELF- ISOLATION IS DANGEROUS
The world is dangerous and enemies are everywhere-everyone has to protect themselves. A fortress seems the safest. But isolation exposes you to more dangers than it protects you from- it cuts you off from valuable information, it makes you conspicuous and an easy target. Better to circulate among people, find allies, mingle. You are shielded from your enemies by the crowd.
LAW 19
KNOW WHO YOU’RE DEALING WITH: DO NOT OFFEND THE WRONG PERSON
There are many different kinds of people in the world, and you can never assume that everyone will react to your strategies in the same way. Deceive or outmaneuver some people and they will spend the rest of their lives seeking revenge. They are wolves in lambs’ clothing. Choose your victims and opponents carefully, then never offend or deceive the wrong person.
LAW 20
DO NOT COMMIT TO ANYONE
It is the fool who always rushes to take sides. Do not commit to any side or cause but yourself. By maintaining your independence, you become the master of others-playing people against one another, making them pursue you.
LAW 21
PLAY A SUCKER TO CATCH A SUCKER: SEEM DUMBER THAN YOUR MARK
No one likes feeling stupider than the next person. The trick, then, is to make your victims feel smart-and not just smart, but smarter than you are. Once convinced of this, they will never suspect that you may have ulterior motives.
LAW 22
USE THE SURRENDER TACTIC: TRANSFORM WEAKNESS INTO POWER
When you are weaker, never fight for honor’s sake; choose surrender instead. Surrender gives you time to re cover, time to torment and irritate your conqueror, time to wait for his power to wane. Do not give him the satisfaction of fighting and defeating you- surrender first. By turning the other cheek you infuriate and unsettle him. Make surrender a tool of power.
LAW 23
CONCENTRATE YOUR FORCES
Conserve your forces and energies by keeping them concentrated at their strongest point. You gain more by finding a rich mine and mining it deeper, than by flitting from one shallow mine to another-intensity defeats extensity every time. When looking for sources of power to elevate you, find the one key patron, the fat cow who will give you milk for a long time to come.
LAW 24
PLAY THE PERFECT COURTIER
The perfect courtier thrives in a world where everything revolves around power and political dexterity. He has mastered the art of indirection; he flatters, yields to superiors, and asserts power over others in the most oblique and graceful manner. Learn and apply the laws of courtiership and there will be no limit to how far you can rise in the court.
LAW 25
RE-CREATE YOURSELF
Do not accept the rol.es that society foists on you. Re-create yourself by forging a new identity, one that commands attention and never bores the audience. Be the master of your own image rather than letting others define it for you. Incorporate dramatic devices into your public gestures and actions-your power will be enhanced and your character will seem larger than life.
LAW 26
KEEP YOUR HANDS CLEAN
You must seem a paragon of civility and efficiency: Your hands are never soiled by mistakes and nasty deeds. Maintain such a spotless appearance by using others as scapegoats and cat’s-paws to disguise your involvement.

From Wilhelm Reich’s “Listen, Little Man” (1945)
LAW 27
PLAY ON PEOPLE’S NEED TO BELIEVE TO CREATE A CULTLIKE FOLLOWING
People have an overwhelming desire to believe in something. Become the focal point of such desire by offering them a cause, a new faith to follow. Keep your words vague but full of promise; emphasize enthusiasm over rationality and clear thinking. Give your new disciples rituals to perform, ask them to make sacrifices on your behalf. In the absence of organized religion and grand causes, your new belief system will bring you untold power.
LAW 28
ENTER ACTION WITH BOLDNESS
If you are unsure of a course of action, do not attempt it. Your doubts and hesitations will infect your execution. Timidity is dangerous: Better to enter with boldness. Any mistakes you commit through audacity are easily corrected with more audacity. Everyone admires the bold; no one honors the timid.
LAW 29
PLAN ALL THE WAY TO THE END
The ending is everything. Plan all the way to it, taking into account all the possible consequences, obstacles, and twists of fortune that might reverse your hard work and give the glory to others. By planning to the end you will not be overwhelmed by circumstances and you will know when to stop. Gently guide fortune and help determine the future by thinking far ahead.
LAW 30
MAKE YOUR ACCOMPLISHMENTS SEEM EFFORTLESS
Your actions must seem natural and executed with ease. All the toil and practice that go into them, and also all the clever tricks, must be concealed. When you act, act effortlessly, as if you could do much more. Avoid the temptation of revealing how hard you work-it only raises questions. Teach no one your tricks or they will be used against you.
LAW 31
CONTROL THE OPTIONS: GET OTHERS TO PLAY WITH THE CARDS YOU DEAL
The best deceptions are the ones that seem to give the other person a choice: Your victims feel they are in control, but are actually your puppets. Give people options that come out in your favor whichever one they choose. Force them to make choices between the lesser of two evils, both of which serve your purpose. Put them on the horns of a dilemma: They are gored wherever they turn.
LAW 32
PLAY TO PEOPLE’S FANTASIES
The truth is often avoided because it is ugly and unpleasant. Never appeal to truth and reality unless you are prepared for the anger that comes from disenchantment. Life is so harsh and distressing that people who can manufacture romance or conjure up fantasy are like oases in the desert: Everyone flocks to them. There is great power in tapping into the fantasies of the masses.
LAW 33
DISCOVER EACH MAN’S THUMBSCREW
Everyone has a weakness, a gap in the castle wall. That weakness is usually an insecurity, an uncontrollable emotion or need; it can also be a small secret pleasure. Either way, once found, it is a thumbscrew you can tum to your advantage.
LAW 34
BE ROYAL IN YOUR OWN FASHION: ACT LIKE A KING TO BE TREATED LIKE ONE
The way you carry yourself will often determine how you are treated: In the long run, appearing vulgar or common will make people disrespect you. For a king respects himself and inspires the same sentiment in others. By acting regally and confident of your powers, you make yourself seem destined to wear a crown.
LAW 35
MASTER THE ART OF TIMING
Never seem to be in a hurry-hurrying betrays a lack of control over yourself, and over time. Always seem patient, as if you know that everything will come to you eventually. Become a detective of the right moment; sniff out the spirit of the times, the trends that will carry you to power. Learn to stand back when the time is not yet ripe, and to strike fiercely when it has reached fruition.
LAW 36
DISDAIN THINGS YOU CANNOT HAVE: IGNORING THEM IS THE BEST REVENGE
By acknowledging a petty problem you give it existence and credibility. The more attention you pay an enemy, the stronger you make him; and a small mistake is often made worse and more visible when you try to fix it. It is sometimes best to leave things alone. If there is something you want but cannot have, show contempt for it. The less interest you reveal, the more superior you seem.
LAW 37
CREATE COMPELLING SPECTACLES
Striking imagery and grand symbolic gestures create the aura of power-everyone responds to them. Stage spectacles for those around you, then, full of arresting visuals and radiant symbols that heighten your presence. Dazzled by appearances, no one will notice what you are really doing.

From Wilhelm Reich’s “Listen, Little Man” (1945)
LAW 38
THINK AS YOU LIKE BUT BEHAVE LIKE OTHERS
If you make a show of going against the times, flaunting your unconventional ideas and unorthodox ways, people will think that you only want attention and that you look down upon them. They will find a way to punish you for making them feel inferior. It is far safer to blend in and nurture the common touch. Share your originality only with tolerant friends and those who are sure to appreciate your uniqueness.
LAW 39
STIR UP WATERS TO CATCH FISH
Anger and emotion are strategically counterproductive. You must always stay calm and objective. But if you can make your enemies angry while staying calm yourself, you gain a decided advantage. Put your enemies off-balance: Find the chink in their vanity through which you can rattle them and you hold the strings.
LAW 40
DESPISE THE FREE LUNCH
‘What is offered for free is dangerous-it usually involves either a trick or a hidden obligation. ‘What has worth is worth paying for. By paying your own way you stay clear of gratitude, guilt, and deceit. It is also often wise to pay the full price–there is no cutting corners with excellence. Be lavish with your money and keep it circulating, for generosity is a sign and a magnet for power.
LAW 41
AVOID STEPPING INTO A GREAT MAN’S SHOES
What happens first always appears better and more original than what comes after. If you succeed a great man or have a famous parent, you will have to accomplish double their achievements to outshine them. Do not get lost in their shadow, or stuck in a past not of your own making: Establish your own name and identity by changing course. Slay the overbearing father, disparage his legacy, and gain power by shining in your own way.
LAW 42
STRIKE THE SHEPHERD AND THE SHEEP WILL SCATTER
Trouble can often be traced to a single strong individual-the stirrer, the arrogant underling, the poisoner of goodwill. If you allow such people room to operate, others will succumb to their influence. Do not wait for the troubles they cause to multiply, do not try to negotiate with them-they are irredeemable. Neutralize their influence by isolating or banishing them. Strike at the source of the trouble and the sheep will scatter.
LAW 43
WORK ON THE HEARTS AND MINDS OF OTHERS
Coercion creates a reaction that will eventually work against you. You must seduce others into wanting to move in your direction. A person you have seduced becomes your loyal pawn. And the way to seduce others is to operate on their individual psychologies and weaknesses. Soften up the resistant by working on their emotions, playing on what they hold dear and what they fear. Ignore the hearts and minds of others and they will grow to hate you.
LAW 44
DISARM AND INFURIATE WITH THE MIRROR EFFECT
The mirror reflects reality, but it is also the perfect tool for deception: when you mirror your enemies, doing exactly as they do, they cannot figure out your strategy. The Mirror Effect mocks and humiliates them, making them overreact. By holding up a mirror to their psyches, you seduce them with the illusion that you share their values; by holding up a mirror to their actions, you teach them a lesson. Few can resist the power of the Mirror Effect.
LAW 45
PREACH THE NEED FOR CHANGE, BUT NEVER REFORM TOO MUCH AT ONCE
Everyone understands the need for change in the abstract, but on the day-to-day level people are creatures of habit. Too much innovation is traumatic, and will lead to revolt. If you are new to a position of power, or an outsider trying to build a power base, make a show of respecting the old way of doing things. If change is necessary, make it feel like a gentle improvement on the past.

From Wilhelm Reich’s “Listen, Little Man” (1945)
LAW 46
NEVER APPEAR TOO PERFECT
Appearing better than others is always dangerous, but most dangerous of all is to appear to have no faults or weaknesses. Envy creates silent enemies. It is smart to occasionally display defects, and admit to harmless vices, in order to deflect envy and appear more human and approachable. Only gods and the dead can seem perfect with impunity.
LAW 47
DO NOT GO PAST THE MARK YOU AIMED FOR: IN VICTORY, LEARN WHEN TO STOP
The moment of victory is often the moment of greatest peril. In the heat of victory, arrogance and overconfidence can push you past the goal you had aimed for, and by going too far, you make more enemies than you defeat. Do not allow success to go to your head. There is no substitute for strategy and careful planning. Set a goal, and when you reach it, stop.
LAW 48
ASSUME FORMLESSNESS
By taking a shape, by having a visible plan, you open yourself to attack. Instead of taking a form for your enemy to grasp, keep yourself adaptable and on the move. Accept the fact that nothing is certain and no law is fixed. The best way to protect yourself is to be as fluid and formless as water; never bet on stability or lasting order. Everything changes.
wilhelm reich on the plague-ridden vs. the living (1945)
Society moulds human character and in turn human character reproduces social ideology en masse. Thus, in reproducing the negation of life inherent in social ideology, people reproduce their own suppression.
Those who are truly alive are kindly and unsuspecting in their human relationships and consequently endangered under present conditions. They assume that others think and act generously, kindly, and helpfully, in accordance with the laws of life. This natural attitude, fundamental to healthy children as well as to primitive man, inevitably represents a great danger in the struggle for a rational way of life as long as the emotional plague subsists, because the plague-ridden impute their own manner of thinking and acting to their fellow men.
A kindly man believes that all men are kindly, while one infected with the plague believes that all men lie and cheat and are hungry for power. In such a situation the living are at an obvious disadvantage. When they give to the plague-ridden, they are sucked dry, then ridiculed or betrayed.
Read the whole of Reich’s essay, “The Emotional Plague” HERE, and an “orgonomic” analysis of mass murders and their relationship to repression HERE (an interesting take in the light of the Orlando nightclub shooting this past weekend, although I completely disagree with the conclusions drawn by the author about what the USA should do about it! I think, frankly, that the USA has an enormous log in its own eye where repression is concerned.)

Diagram by Wilhelm Reich depicting his theory of the antithetical functional unity between instinct and defense, and illustrating specific impulses.
[EDIT, 14 June 2016]: From Facebook this morning:

a lacanian interpretation of sartre’s ‘erostratus’ (1939)
Read Jean Paul Sartre’s short story Erostratus, written the year after his famous Nausea, HERE.
Jordan Alexander Hill on the story from a psychoanalytical perspective:
Jean-Paul Sartre’s “Erostratus” may be the shortest story in The Wall, yet it serves as a fitting psychoanalytic case-study. “Erostratus” tells the story of Paul Hilbert, a lonely man plagued by insecurity and sexual impotency, who attempts and ultimately fails to commit a heinous crime. Shortly into the story, it becomes clear that the crime is mostly an attempt to escape his mediocrity through an act of powerful self-assertion. We will look at this story not only through a traditional psychoanalytic lens, but also by applying important Lacanian principles. Sartre, who developed his own “existential” brand of psychoanalysis, surely wrote “Erostratus” to support certain phenomenological and ethical themes from Being and Nothingness—we’ll look at some of these perspectives. However, in many ways, we arrive at the deepest understanding of Hilbert and his motivations by bringing Lacanian theories into the discussion. In this paper, we first locate the basic existential and psychoanalytic themes that underpin “Erostratus”, in addition to looking at Lacan’s “mirror phase” and how this relates to Hilbert’s social development. “Erostratus” is essentially a story about narcissism, alienation, otherness, and desire. Lacan’s psychic structures—particularly the imaginary and symbolic orders—will give us a sense of where these emotions come from, how they affect our protagonist, and how they function in the larger narrative.
Like in many “existential” works, our protagonist is a bland working class guy with a routine existence and a mundane job. He has no friends to speak of and is a self-professed “anti-humanist”. As Hilbert’s impatience with his situation grows, he decides he must make a statement that will prove his anti-humanism and secure his name in the history books—he will murder six random people on a busy street in Paris. Hilbert is deeply moved by the ancient Greek story of “Erostratus,” which tells of a man who burned down the temple of Artemis at Ephesus to immortalize himself. What strikes him is that while nobody knows the name of the man who built the temple of Artemis, everyone remembers Erostratus, the man who destroyed it. The rest of the story follows Hilbert’s metamorphosis, as the day of his crime draws nearer. In what follows, Hilbert buys a gun and carries it around in public, becoming sexually aroused by the possibilities, and the power he now possesses. He becomes more and more obsessed with this power and even visits a prostitute, commanding her to walk around naked at gunpoint (he does this several times, each time ejaculating in his pants). As the day of his crime draws nearer, Hilbert spends his life savings on expensive meals and prostitutes, and even mails letters of his murderous intent to 102 famous French writers. Yet, in the end, Hilbert is incapable of following through. He winds up shooting only one man, a “big man”, and has a frantic meltdown in the street afterward. The story ends in a café lavatory, as Hilbert gives himself up to the police.
Let us first take a look at some of the elements that make up the “existential” composure of the story. Hilbert’s act of mailing letters to famous writers before committing his crime shows a deep insecurity over the potential legacy he wishes to leave. Hilbert must have others verify and be witness to his crime for the weight of his actions to seem real to him. In existential thought, this is an offense known as “being-for-others” (we’ll return to this later when we discuss Lacan). Hilbert no longer lives in a world where his actions and choices hold any real weight or significance. This lack of self-determination plunges Hilbert into a kind of moral nihilism, which only exacerbates his problems. Another significant element to note is the rise in power Hilbert feels as he buys a gun and brings it around with him wherever he goes. The angst or dread that follows—often described in existential circles as being a kind of “excitement or fear over the possibility of one’s own freedom”—is an important aspect of Hilbert’s condition. Furthermore, one would not have to use queer theory, nor is it beyond any stretch of the imagination, to assert that Sartre uses the gun here as a phallic symbol. For Hilbert, happiness truly is a warm gun, as the gun symbolizes the power he has always lacked socially and sexually. The fact that Hilbert makes prostitutes walk around naked at gun point, without letting them touch or look at him, is another teller. This voyeuristic behavior, according to Sartre, is a mechanism by which the individual avoids his or her own subjectivity—shirking responsibility—in order to live through the imagined subjectivity of another (Sartre, 1953, 244). Hilbert, it turns out, suffers in large part from a staggering lack of being (this “lack of being” doesn’t stem from any shortage of self-consciousness, but rather from a case of what I’ll call “mistaken identity,” in a Lacanian sense).
Hilbert’s crime, we come to find out, is not motivated by material gain or political ideology. What, then, is it motivated by? To start, let’s look at our protagonist’s own self-identification: Hilbert believes his crime is motivated by his “anti-humanism”. In the letter, he congratulates the famous authors for being humanists, for loving men. “You have humanism in your blood…” Hilbert writes, “You are delighted when your neighbor takes a cup from the table because there is a way of taking it which is strictly human… less supple, less rapid than that of a monkey”. He goes on to sarcastically praise the authors for relieving and consoling the masses. “People throw themselves greedily at your books… they think of a great love, which you bring them and that makes up for many things, for being ugly, for being cowardly, for being cuckolded, for not getting a raise on the first of January”. These sound like Hilbert’s own problems.
Later in the letter, Hilbert explains his own hatred of humanity. “I cannot love them… what attracts you to them disgusts me… men chewing slowly, all the while keeping an eye on everything, the left hand leafing through an economic review. Is it my fault I prefer to watch the sea-lions feeding?”. Given this, it would be a mistake to equate Hilbert’s anti-humanism to misanthropy. The word “misanthrope” is normally an intellectual self-label, which is defined by a general disgust with the thoughtlessness or lack of social awareness perceived in others. As Moliere notes in his Les Misanthrope: “I detest all men; Some because they are wicked and do evil, Others because they tolerate the wicked” (Moliere, I.i.). Hilbert, on the other hand, is not a misanthrope; he is a self-reflective watcher, a voyeur. And his anti-humanism—his “all-too-humanness” as he puts it it—seems to involve the hatred of those physical and emotional qualities which he observes in others, and which he himself cannot experience. Hilbert’s condition is strikingly similar to Sartre’s analysis of the poet Baudelaire. “For most of us,” Sartre contends, “it is enough to see the tree or house; we forget ourselves” (Sartre, 1950, 22). Baudelaire, however, “was the man who never forgot himself” (Sartre, 1950, 22). Hilbert, likewise, is too self-conscious to experience normal human emotions. He does not simply see things; but sees himself seeing things. As such, he has lost the unselfconscious grace and naturalness he so despises in others.
This deep self-consciousness, this narcissism, is something that alienates Hilbert, and makes normal communication with others almost impossible. If we asked Lacan, he would probably point us to the mirror phase and the imaginary order, which are both significant in Hilbert’s case. The mirror phase refers to a period in psychosexual development, when “the child for the first time becomes aware, through seeing its image in the mirror” (Homer 24). For Lacan, this marks the emergence of the ego, as the child realizes it can control the movements of this new image. This should not be confused with the advent of “selfhood,” but rather it is a moment of profound alienation, where we actually mistake this new mirror-image for our “self” (Homer 25).
Read more of this article HERE (and read the actual story HERE).
on undoing the self and paying attention
 Excerpted from this post at Wine, Women and Philosophy:
Excerpted from this post at Wine, Women and Philosophy:
… And aren’t unsettling folk just like that? You think you’ve done them, ticked them off, when suddenly, you’re back to square one… This other quagmire into which we had unwittingly waded – the actual technicalities involved in “undoing the creature in us” so as to successfully “decreate” a la Weil – required our immediate attention.
And so, spurred on by Anne Carson’s insight into how to go about actually paying attention – “Attention is a choice of where you put your mind…And looking at the object of your attention to the extent that you forget you’re doing the looking” – we embarked on a series of exercises designed to both instruct us on the ins and outs of destroying the “I,” and sharpen our skills in the attentiveness department.
Of course, there was a lot of preliminary discussion as to whether destroying the “I” was a desirable thing in the first place. In a sense, that Weilian notion of carving out a void in the space where the self normally resides goes counter to the rah-rah-be-your-biggest-and-best-self kind of rhetoric on offer in Self-Esteem for Dummies etc. In a culture where Self reigns Supreme, doing away with it is unnerving at best, terrifying at worst – even if this negation is, as Weil contends, a necessary move if one is to fully open oneself to Truth and Knowledge and Whatever Else Truly Matters.
For the self gets in the way. Like a shadow, it blocks out the light. Like unwanted baggage, it weighs you down. Like the elephant in the room, it takes up all the space. Clear the shadow, the baggage, the elephant, and you’re starting to get somewhere. A strange way to go about getting to the bottom of self-esteem, perhaps. But it seemed to offer something in the way of getting more out of life, and so we bit.
Simone Weil suffered from terrible migraines. She tried many ways of clearing them out of her head, but nothing seemed to work. One thing she knew for sure was that they got in the way of her being able to turn her full attention to what mattered. In April 1938 she found herself attending the Easter Mass at the Abbeye St-Pierre in Solesmes. She felt the Gregorian chanting of the monks enter her body, go straight to the space in her head filled with migraine. As the chanting poured in, her migraine did a peculiar thing: it emptied out. Soon, the space formerly known as migraine was awash with Gregorian Chant. It was a space rendered ready for paying attention: for “a patient holding in the mind,” as Weil referred to the act of paying attention, which in turn would make thought itself “available, empty, penetrable by the object.”
This is a radical take on the role of thought in the life of the mind: not the light bulb switching on as it encounters its object, but rather, the necessary conditions for the object to come to light. In Weil’s conception, thought must be suspended if the object of one’s attention is to find its way in, gain a proper foothold. If thought is busy thinking, the object just passes it by. If thoughtfulness hasn’t twinned itself up with attentiveness, the best we can hope for when it comes to thinking is a worrying – Weil would go so far as to say dangerous – mishmash of “partial attitudes.”
That, at least, is the theory. We obviously needed to put ourselves in Weil’s shoes to grasp what it felt like in practice. And so we experimented with filling our heads with the self-same Gregorian chants that had so impacted Weil, and making of the resulting void a luminous object-ready nesting ground. Yah, right. Weil, as I suggested earlier, was unsettling: not your average, run-of-the-mill, kind of gal.
But we gave it a go, and then turned our attention to other aural stimuli: a metronome’s steady tick-tocking, which brought the Weilian notion of time as “unvarying perpetuity” into the equation; a wind-up music box with its twirling ballerina and its ever-decelerating ditty, which prompted us to probe yet further how time, if invariably monotonous for Weil, could helpfully be categorized as either “time surpassed” – as in here comes the void, which is good monotonous – or as “time sterilized” – as in me just going round and round like “a squirrel turning it its cage” and never getting anywhere near the void, much less admitting to myself that I am going round and round (which for Weil is the worst sin of all, this kind of self-delusion) and which is, not surprisingly, bad monotonous.
This seemed as good a queue for a song as we were likely to get, so we broke out Anne Carson’s Duet of What is a Question from her Weil-inspired opera in three parts, Decreation (2005), and gave it our valiant best. Improvising the vocal arrangements – Carson had only supplied the libretto – provided us with the perfect opportunity to pay attention to each other, and hone our deep listening skills. As for getting us closer to the void, we were still a little in the dark. Enter American poet Fanny Howe (b.1940) and her beautifully observed prose poem, Doubt.
If Baruch Spinoza is the physicists’ philosopher, Simone Weil, it would seem, is the poets’ philosopher. Though it is easy to understand why Weil speaks to poets like Carson and Howe, the writing that comes of their interest in her ideas and her personal narrative is as tantalizing and challenging as Weil herself.
Sometimes, though, what poetry gives us that philosophy cannot is a line of such stark and heart-breaking beauty that knowing what the void, for example, actually is, or what it is to make one or find it or get there no longer seems to matter. For a very brief moment, we just feel decreated – like the creature in us has unraveled, like we have completely come undone.